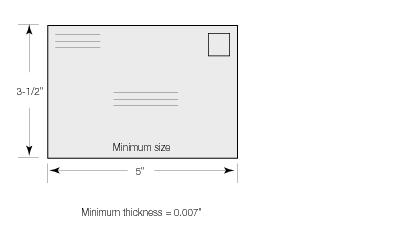
DMM TOC > 600 Basic Standards for All Mailing Services601 Mailability3.0 Acceptable Mailing Containers 4.0 Cushioning, Closure, and Reinforcement 5.0 Handling, Content, and Extra Service Markings 6.0 Mailing Containers—Special Types of Envelopes and Packaging 7.0 Packaging Standards for Mail Processed at Network Distribution Centers 8.0 Nonmailable and Restricted Articles and Substances Generally 11.0 Cigarettes and Smokeless Tobacco 1.0 General Standards1.1 Determining Mail Processing CategoriesThere are five mail processing categories for mailpieces: letter, flat, machinable parcel, irregular parcel, and outside parcel. USPS assigns each mailpiece to one of these categories based on the physical dimensions and characteristics of the mailpiece using the longest dimension as the length, regardless of the placement or orientation of the delivery address on the piece. For example, a mailpiece that is 5 inches by 8 inches and at least 0.007 inch thick is within the range of letter-size dimensional standards in 101 and 201. See the physical standards for processing categories in 101 for retail (single-piece price) mail, 201 for discount letters, 301 for discount flats, and 401 for discount parcels. 1.2 Minimum Dimensions[1-22-12] For mailability, the following standards apply: a. All mailpieces must be at least 0.007 inch thick. b. All mailpieces (except keys and identification devices) that are 1/4 inch thick or less must be: 1. At least 3-1/2 inches high and at least 5 inches long. 2. Rectangular, with four square corners and parallel opposite sides (see Exhibit 1.2b2), or with finished corners and parallel opposite sides under 1.2b..3. or 1.2b..4., unless prepared as Customized Market Mail under 705.1.0.
Exhibit 1.2b2
Minimum Dimensions, Pieces 1/4" Thick or Less
3. Letter-size, card-type mailpieces made of cardstock and flat-size mailpieces may have finished corners that do not exceed a radius of 0.125 inch (1/8 inch). See Exhibit 1.2b3.
Exhibit 1.2b3
Maximum Corner Radius
4. Except for machinable parcels described in 401.1.5.2, pieces mailed at parcel prices may have finished corners that do not exceed a radius of 0.5 inch (1/2 inch). See Exhibit 1.2b4.
Exhibit 1.2b4
Maximum Corner Radius for Parcels
1.3 Maximum Dimensions and WeightNo mailpiece may weigh more than 70 pounds. Except for Parcel Post, no mailpiece may measure more than 108 inches in length and girth combined. For parcels, length is the distance of the longest dimension and girth is the distance around the thickest part. 1.4 Length and Height[1-22-12] Determine the processing category (see 1.1) based on the physical dimensions and characteristics of the mailpiece, without regard to address placement. Then, determine length and height as follows: a. Letter-size pieces. For the purpose of determining mailability or machinability (see 1.5), the length is the dimension parallel to the delivery address as read; the height is the dimension perpendicular to the length. b. Flat-size pieces. The length of a flat-size mailpiece is the longest dimension. The height is the dimension perpendicular to the length. c. Parcels. The length is the longest dimension. d. Customized MarketMail pieces. See 705.1.0. 1.5 Nonmailable and Nonmachinable Placement of AddressThe placement of the address on a letter-size mailpiece may render a piece nonmailable or nonmachinable. If the length (the dimension parallel to the address) of a letter-size mailpiece is not at least 5 inches, it is nonmailable. If the height (the dimension perpendicular to the length) of a letter-size mailpiece is not at least 3-1/2 inches, it is nonmailable. If the aspect ratio (length divided by height) is not within 1.3 to 2.5 (inclusive), the piece is a nonmachinable letter. For example: a. For a letter-size piece that is 4 inches by 6 inches, if the address is parallel to the 4-inch dimension, it is 4 inches long, which is less than the minimum length of 5 inches required in 1.2. Therefore, this piece is nonmailable. b. Following the process in 1.1, a piece that is 5 inches by 8 inches (and within letter-size thickness dimensions) is a letter. If the address is parallel to the 8-inch dimension, the piece is 8 inches long and 5 inches high. The aspect ratio of this piece is 1.6, so it is a mailable letter within machinable dimensions for length and height. c. For a letter-size piece that is 5 inches by 8 inches, if the address is parallel to the 5-inch (shorter) dimension, the piece is 5 inches long and 8 inches high. The aspect ratio of this piece is 0.625, which is not within 1.3 to 2.5, so it is mailable as a nonmachinable letter. 1.6 General Mailability and Right of RefusalArticles presented for mailing must be prepared under the general and specific standards in this document. The USPS accepts properly packaged and marked parcels but reserves the right to refuse nonmailable or improperly packaged articles or substances. Additional or other standards can apply to overseas military Post Offices and international mail. 1.7 Mailer’s ResponsibilityIt is the mailer’s responsibility to refrain from depositing nonmailable matter in the mail. The mailer must comply with applicable postal laws and regulations governing mailability and preparation for mailing, as well as nonpostal laws and regulations on the possession, treatment, transmission, or transfer of particular matter. Information about USPS standards is available from postmasters, business mail entry managers, and the PCSC manager (see 608.8.0, USPS Contact Information). 2.0 Packaging2.1 GeneralMailers must package mailpieces to withstand normal transit and handling without content or package breakage, injury to USPS employees, or damage to other mail. Mailers also must package contents to prevent their deterioration. See 2.2 through 2.8 for specific types of items. Mailers must follow these additional general standards for packaging: a. Cushion fragile items to withstand handling in processing, transportation, and delivery. b. Package contents so they do not shift within the mailing container. c. Brace and cushion heavy items to prevent damage to other mailpieces. 2.2 StationeryStationery-type items thicker than 1 inch or heavier than 1 pound are not accepted in letter-style envelopes. The contents of these packages must be secured by tying, banding, or using partitions on close-fitting interior containers to prevent shifting. 2.3 Odd-Shaped Items in Paper EnvelopesPens, pencils, key rings, bottle caps, and other similar odd-shaped items are not permitted in letter-size or flat-size paper envelopes unless they are wrapped within the other contents of the envelope to streamline the shape of the mailpiece and prevent damage during postal processing. If an odd-shaped item is not properly wrapped, it could burst through the envelope and cause injury to employees and damage to USPS processing equipment. Odd-shaped items that are properly wrapped within paper envelopes and sent at letter prices may be subject to the nonmachinable surcharge under 133.1.5 or 233.4.3 for First-Class Mail letters, or the nonmachinable prices under 243.5.5 for Standard Mail letters. Certain types of odd-shaped items, when properly wrapped, are permitted as automation price letter-size mail subject to the standards in 201.3.0. Flat-size automation price mail is subject to the uniform thickness requirement in 301.3.0. 2.4 LiquidsMailers must mark the outer container of a mailpiece containing liquid to indicate the nature of the contents. Mailers must package and mail liquids under the following conditions: a. Use screw-on caps, soldering, clips, or similar means to close mailpieces containing liquids. Do not use only friction-top closures (push-down types). b. Liquids in steel pails and drums with positive closures, such as locking rings or recessed spouts under screw-cap closures, may be mailed without additional packaging. c. Package glass and other breakable containers of liquid with a capacity of more than 4 fluid ounces according to the following requirements: 1. Cushion the primary container with material sufficient to absorb all leakage in case of breakage. 2. Place the primary container inside another sealed, leakproof container (secondary container), such as a can or plastic bag. 3. Use an outer mailing container that is strong enough to protect the contents. d. As an alternative to 2.4c. above, mailers may use containers certified by the International Safe Transit Association (ISTA) that passed ISTA's Test Procedure 3A. Mailers must provide their ISTA 3A Package-Product Certification Notice at the time of mailing as verification that the mailpieces they are submitting passed the required performance test. 2.5 AerosolsAerosols (containers under pressure) are hazardous materials and must be constructed to prevent accidental discharge of the contents during postal handling. Mailable aerosol containers must be packaged under 10.12. 2.6 Perishable, Hazardous, and Restricted ItemsMailpieces containing perishable, hazardous (including infectious substances), biological, or restricted materials are subject to standards in 8.0 through 12.0. 2.7 High-Density ItemsHigh-density items are solid objects (such as tools, hardware, and machine and auto parts) whose weights are comparatively high for their volumes. Package high-density items weighing more than 15 pounds so that the contents do not exert more than 60 pounds per square foot on the smallest side of the mailing container. 2.8 Load TypeThe following three terms describe types of loads, based on content, degree of protection, and strength of the mailing container. a. An easy load contains items of moderate density that either completely fill the mailing container or are packaged in interior containers that completely fill the mailing container. Easy load items are not easily damaged by shock, compression, or puncture. b. An average load contains moderately concentrated items packaged directly into a mailing container. Mailers can prepackage average load contents by nesting items within partitions or in separate paperboard boxes to stabilize items to prevent shifting and damage. c. A difficult load contains items that require a high degree of protection to prevent shock, puncture, or distortion to the items or the mailing container. The Postal Service does not accept in paperboard boxes, bags, or wraps difficult loads such as fragile items; delicate instruments; and high-density, small-bulky items. 3.0 Acceptable Mailing Containers3.1 EnvelopesMailers must prepare envelopes according to the following weight limits and conditions: a. For mailpieces weighing no more than 1 pound and measuring no more than 1 inch thick, mailers may use letter-style (flat, nonreinforced) envelopes for stationery and similar nonrigid material. b. For mailpieces weighing more than 1 pound up to 5 pounds or measuring more than 1 inch thick, mailers may use envelopes if they are sturdier than nonreinforced letter-style envelopes. Acceptable envelopes include those made either from paper equivalent to 28-pound basis weight (or greater) or from extra-strength materials with a Mullen strength of more than 90 pounds per square inch. c. Mailers may use envelopes for odd-shaped items if the mailpiece meets the standards for the class of mail (see 2.3). d. Envelopes for photographic film are acceptable if made from paper equivalent to 24-pound basis weight or greater. 3.2 BoxesBoxes are acceptable, subject to these standards: a. Paperboard boxes may be used for easy and average loads to 10 pounds. b. Metal-stayed paperboard boxes may be used for easy and average loads to 20 pounds. c. Solid and corrugated fiberboard boxes may be used according to the limits in the following chart, unless otherwise specified. The first maximum reached governs the grade of the box used.
d. Wood, metal, or plastic boxes may be used for all types of loads, assuming adequate construction. e. The size of the box must be adequate to contain the items and provide enough space for cushioning material. f. Good, rigid, used boxes with all flaps intact are acceptable. g. Boxes with difficult loads to out-of-town destinations must be reinforced with banding about every 8 inches in each direction around the package. 3.3 Fiberboard Tubes and Similar Long ContainersMailers may use fiberboard tubes and similar lengthy containers for mailing if the containers meet the following requirements: a. The length must not exceed 10 times the girth. b. When using friction slide closures as end caps, reinforce closures by encircling all seams with tape. Crimped or taped end closures are acceptable only for lightweight rolled items (such as posters or charts). c. The strength of the tube ends must be at least equal to the tube sidewall strength, unless the contents are lightweight rolled items. d. Sidewall strength of tubes must be equal to solid fiberboard that is: 1. At least 1/16 inch thick for tubes less than 18 inches long. 2. At least 3/32 inch thick for tubes 18 to 32 inches long. 3. At least 5/32 inch thick for tubes more than 32 inches long. 3.4 Paper Bags and WrapsFor easy loads of up to 5 pounds, paper bags and wraps are acceptable when at least of a 50-pound basis weight (the strength of an average large grocery bag) and the items are immune from impact or pressure damage. A combination of plies adding up to or exceeding 50-pound basis weight is not acceptable. For easy and average loads of up to 20 pounds, reinforced bags or bags with a minimum of 70-pound basis weight are acceptable. Nonreinforced loose-fill padded bags are not acceptable as exterior containers, unless the exterior ply is at least 60-pound basis weight. 3.5 Plastic BagsPlastic bags must be at least 2 mil thick polyethylene or equivalent for easy loads up to 5 pounds; 4 mil thick for easy loads up to 10 pounds. 3.6 Plastic FilmHeat-shrinkable plastic film—either irradiated polyethylene, linear low-density polyolefin, or copolymer—may be used as packaging for mailpieces under the following conditions only: a. Film must be at least 3/4 (0.75) mil thick for an easy load up to 5 pounds. b. Film must be at least 1-1/4 (1.25) mil thick for an average load up to 5 pounds. c. Film must be at least 1-1/2 (1.5) mil thick for an average load parcel up to 10 pounds, only when mailers prepare the parcels on 5-digit/scheme, merged 5-digit/scheme, or finer level pallets. d. When requested, mailers must provide written certification that these types of film are being used. 3.7 Cloth BagsCloth bags are acceptable for easy and average loads of up to 10 pounds, if the seams of the bags equal the strength of the basic material. 3.8 Difficult LoadThe USPS does not accept bags, bales, or wraps with difficult loads. The contents in bags, bales, and wraps must be compressed when possible. 3.9 BalesBales are acceptable within postal weight limits, if adequately compressed and reinforced to contain the material. 3.10 Cans and DrumsMailers may mail items in cans and drums with positive closures (such as clips). Friction closures alone are not acceptable. Mailers must shield protruding devices, such as locking rings, with padding material to prevent injury to USPS employees and damage to equipment or other mail. 4.0 Cushioning, Closure, and Reinforcement4.1 VolumeLoose-fill cushioning must overfill the container before closure to hold the item and prevent its movement to an outside surface of the container or to other items in the package. Shock and pressure forces must be dissipated over as much of the surface of the item as possible. 4.2 Multiple Items Within ContainerWhen multiple items are inside a single mailing container, mailers must cushion items to protect them from each other as well as from external forces. Do not package high-density heavy items with fragile items unless extreme care is taken to separate them from each other. Mailers must adequately stabilize heavy items within the package. 4.3 TapeCellophane and masking tape may not be used for closure or reinforcement of packages but may be used to augment adhesive closures on envelopes or to cover staples on bags. 4.4 Paper TapePaper tape must be at least 60-pound basis weight kraft. The adhesives on gummed tapes must be adequately activated before application and firmly applied with the tape extending at least 3 inches over the adjoining side of the box. 4.5 Tape SizeExcept for pressure-sensitive filament tape, tapes used for closure and reinforcement may not be less than 2 inches (or 48 mm metric) wide. Nonreinforced plastic tapes must be at least as strong in the cross direction as in the machine (long) direction. 4.6 AdhesiveAdhesives used for closure on box flaps or on tapes must remain serviceable from -20 degrees to +160 degrees Fahrenheit. When using hot-melt adhesive, apply adhesive using one of these methods: a. Apply hot-melt adhesive to 25% of the area where the outer flap lies over the inner flap. b. Apply at least four strips of hot-melt adhesive on each part of the box flap where the outer flap overlays the inner flap as follows: 1. Use strips at least 3/16 inch wide after compression. 2. Place the strips not more than 1-1/2 inches apart, with the first strip no more than 1/2 inch from the center seam. 3. Place all strips along the full width of the inner flap. 4.7 BandingWhen banding is used for closure and reinforcement, it must encircle the length and girth of the package at least once. If twine or cord is used for closure and reinforcement, it must be at least 20-pound tensile strength and secured at an intersection at least once on each side. Loose strapping and metal strapping are not acceptable. 4.8 Staples and Steel StitchingMailers may use staples or steel stitching to close boxes as follows: a. Place the staples or stitching within 1-1/4 inches from the ends of the box. b. Space staples or steel stitches not more than 5 inches apart for easy and average loads and not more than 2-1/2 inches apart for difficult loads. If placing staples farther apart, apply strips of 3-inch-wide reinforced tape in the gaps between the staples. c. Tightly clinch staples to prevent protrusions. Mailers must remove and replace inadequately clinched staples before mailing. 5.0 Handling, Content, and Extra Service Markings5.1 Handling, Content, and Extra ServiceCertain markings may be used to identify handling, content, and extra service. Unauthorized markings not designating price, class, address, handling, content, or extra service are not permitted. Extraneous information, which can be confused with ZIP Codes, may not be placed next to or directly under the last line of the delivery address. Any obsolete marking on a container to be reused for mailing must be obliterated. The following markings must be placed in an area below the postage and above the addressee’s name in the delivery address and to the right of the return address: a. Handling markings such as “Fragile” must be applied only to packages containing delicate items such as glass and electrical appliances. b. Content markings such as “Perishable” must be applied to any package containing items or substances that can degrade or decompose rapidly such as meat, produce, plants, or certain chemical and hazardous materials samples. Restricted and hazardous articles must be marked and labeled under applicable standards. A container improperly identified by content is not acceptable for mailing (e.g., a box marked “Art Supplies” that contains flammable liquid or a box marked “Bleach” that contains clothing). c. Extra service markings such as “Return Receipt Requested” must use the wording or label required by the applicable extra service standards. 5.2 MethodThe mailer must mark the package using material that is not readily water soluble or easily smeared or rubbed off. The marking must be readable at a distance of 30 inches. Marking methods or surfaces must permit application and retention of adhesive stamps, postage meter impressions, and postal endorsements made with hand stamp, ballpoint pen, or Number 2 pencil. Any address label or envelope must be firmly affixed to the mailing container, with no more than an 1/8-inch separation between the ends of the label or envelope and the container. 6.0 Mailing Containers—Special Types of Envelopes and Packaging6.1 Express Mail and Priority Mail PackagingExpress Mail and Priority Mail packaging provided by the USPS must be used only for Express Mail or Priority Mail, as applicable. Regardless of how the packaging is reconfigured or how markings may be obliterated, any matter mailed in USPS-provided Express Mail or Priority Mail packaging is charged the appropriate Express Mail or Priority Mail price. 6.2 6.2 Critical Mail EnvelopesCritical Mail letter-size and flat-size envelopes are provided by USPS and must be used only for Critical Mail. Use of these envelopes is restricted to eligible matter and postage payment methods (see 224.1.1 and 324.1.1). Matter mailed in USPS-produced Critical Mail envelopes that do not meet the criteria for Critical Mail are charged the appropriate Priority Mail Commercial Plus Flat Rate Envelope prices (volume thresholds apply). 6.3 Green Diamond Border EnvelopeAn envelope or card bearing a green diamond border must be used only for First-Class Mail. Any envelope or card bearing a green diamond border is charged the appropriate First-Class Mail price, regardless of mail content or of requested class or service. When printed on letter-size mail, the border must not enter the OCR read area or barcode clear zone unless a delivery point barcode appears in the address block as described in 202.5.7. 6.4 Window EnvelopeFor all letter-size and flat-size mail in window envelopes, every character in the delivery address, including any postal barcode, marking, or endorsement, must be completely visible through the window throughout the full range of movement of the insert bearing the delivery address. Any window envelope used for letter-size or flat-size mail claimed at automation prices or for letter-size mail claimed at Enhanced Carrier Route high density or saturation prices must also meet the barcoding standards for letters and flats in 708.4.0. Any window envelope used for letter-size or flat-size mail must meet the following additional standards: a. The address and any barcode visible through the window must be printed on white paper or paper of a very light color. b. A clear space of at least 1/8 inch is required between the address block, which includes any optional endorsement line, and the top, bottom, and left and right edges of the address window, and must remain when the insert is moved to its full limits in each direction within the envelope to ensure efficient processing and delivery. See 202.5.7 (letters) or 302.5.6 (flats) for barcode clearances when the address block contains a barcode. For nonautomation price mail, the bottom edge of the address window must not extend more than 1/8 inch into the barcode clear zone as defined in 202.5.1. Any letter-size envelope containing a window that intrudes into the barcode clear zone is not eligible for MLOCR or RVE FASTforward processing options for the Move Update standard in 233.3.5. c. Window cover material, if used over the address window, must be made of a nontinted clear or transparent material (e.g., cellophane or polystyrene) and must permit the address, as viewed through the window material, to meet the print contrast ratio (PRC) standards in 708.4.0 to ensure efficient processing and delivery. Glassine may be used for window cover material. All edges of the window cover material must be glued securely to the envelope. The bottom edge of an address window must be at least 1/2 inch from the bottom edge of the envelope. d. For letter-size mail, the delivery address window must be parallel with the longest edge of the envelope. For flat-size mail, the address window may be parallel with any edge of the envelope. e. For Registered Mail, the opening on a window envelope must be covered as described in 503.2.4.8. 6.5 Reusable MailpieceA reusable mailpiece is an envelope, self-mailer, or similar mailpiece designed for two-way mailing. The recipient removes part of the original mailpiece or refolds the piece to cover the delivery address of the recipient and reveal the delivery address of the originator (sender) for return. Except for reusable mailpieces that originate as permit imprint mailings, the piece must meet these standards: a. Basic Design. The piece must be designed and constructed to allow the recipient to reconfigure or modify the piece to remove or obscure the address, POSTNET barcode, postage, and any marking or endorsement that applied to the piece when it was originally mailed so that these elements are not mistaken by USPS employees or mail processing equipment as applying to the returned piece. The instructions on the piece must ensure that the recipient can prepare the piece correctly for remailing. If a reusable mailpiece does not meet the applicable standards, the piece must be re‑enveloped and new postage affixed before distribution by the originator. b. Distribution. When the piece is mailed by the originator, the piece must show only one complete delivery address and, if used, the corresponding barcode; the appropriate postage; and any required marking or endorsement. The originator’s address and barcode for returning the piece and any postage, marking, endorsement, and facing identification mark (FIM) provided for that purpose must be obscured so that they are not mistaken by USPS employees or postal mail processing equipment as applying to the originating piece. c. Return. When the piece is reconfigured for return from the recipient to the originator, the piece must show only one complete delivery address and, if used, the corresponding barcode; the appropriate postage; and any required marking, endorsement, and FIM. If a reusable mailpiece does not meet the applicable standards, the piece must be re‑enveloped and new postage affixed before return by the recipient. 6.6 Alternative Reusable Mailpieces That Originate as Permit Imprint Mailings6.6.1 Basic DesignThe piece must be designed and constructed so that the recipient may reconfigure or modify it to remove or obscure the address that applied to the piece when it was originally mailed. The instructions on the piece must ensure that the recipient can prepare the piece correctly for remailing. If a reusable piece does not meet the applicable standards, the piece must be re‑enveloped and new postage affixed before distribution by the originator. 6.6.2 DistributionWhen reusable mailpieces are originally mailed, postage must be paid with permit imprint and a complete address and corresponding barcode must be located in the address block. Reusable pieces must be entered at a postal facility as part of a permit imprint mailing. On mailpieces other than window envelopes, the address block for return of the piece (including the delivery address and a corresponding barcode) will be located on the reverse side. If included, prepaid reply postage must be located or obscured so that it is not mistaken by postal mail processing equipment or employees as applying to the originating piece. 6.6.3 ReturnWhen the piece is reconfigured for return from the recipient to the originator, only one complete address with a corresponding barcode located in the address block and a FIM must be visible on the piece. If a reusable mailpiece does not meet the applicable standards, the piece must be re‑enveloped and new postage affixed before return by the recipient. 6.6.4 Two-Way IndiciaWhen the permit imprint indicia for Standard Mail or First-Class Mail is printed on a reusable window envelope intended to be returned as Business Reply Mail (BRM), the imprint “NO POSTAGE NECESSARY IF MAILED IN THE UNITED STATES” must be printed on the envelope directly below the permit imprint indicia. See Exhibit 601.6.6.4 below. These additional conditions apply: a. The permit imprint indicia must be located in the upper right corner of the address side of the mailpiece. b. The horizontal bars must be printed directly below the “NO POSTAGE NECESSARY” imprint and must not extend below the delivery line of the address. c. The other BRM elements as described in 505.1.8, with the exception of the Facing Identification Mark (FIM), must appear on the insert in the envelope window. The FIM C must be printed on the envelope under 708.9.0. d. The outgoing First-Class Mail portion with two-way indicia must be endorsed “Return Service Requested,” except for mailpieces participating in Address Change Service (ACS). First-Class Mail letters participating in ACS must be endorsed “Change Service Requested” for traditional ACS. Mailpieces with Intelligent Mail barcodes and requesting OneCode ACS must have the printed endorsement “Electronic Service Requested,” but the embedded request must be for “Change Service Requested” (option 1) only. Endorsements must not appear directly below or to the left of the postage area, and must not be visible when the mailpiece is configured for reply purposes (see 507.4.2 and Exhibit 507.1.5.1). e. Standard Mail with two-way indicia should not be forwarded, and must not be endorsed “Address Service Requested” or “Forwarding Service Requested.”
Exhibit 6.6.4
Outgoing and Return Two-Way Indicia Examples 7.0 Packaging Standards for Mail Processed at Network Distribution Centers7.1 High-Density ItemsHigh-density items (see 2.7) weighing from 20 to 45 pounds must be packaged in fiberboard boxes constructed of a minimum 200-pound test board or equivalent wood, metal, or plastic containers. Plastic, metal, and similar hard containers must be packaged, treated, or otherwise prepared so that their coefficient of friction or ability to slide on a smooth, hard surface is similar to that of a domestic-class fiberboard box of the same approximate size and weight. Closure must be done by staples, heat-shrinking, adhesives, or tape. Boxes without inner packing or containing loose material must be reinforced or banded with reinforced paper or plastic tape, pressure-sensitive filament tape, or firmly applied nonmetallic banding. Internal blocking and bracing, including the use of interior containers, cut forms, partitions, dunnage, and liners, must be used as required so that packages are capable of maintaining their integrity without damage to the contents if dropped once on one of their smallest sides on a solid surface from a height of 3 feet. These items from 45 to 70 pounds must be similarly packaged, closed, and reinforced, except that exterior containers must be a minimum of 275-pound test fiberboard or equivalent. 7.2 BooksBooks and similarly produced printed matter (such as catalogs) fastened together along one edge between hardback, paperback, or self-covers, that are more than one inch thick or one pound must not be accepted in letter-style non-reinforced flat envelopes or without packaging. Envelopes meeting the standards in 3.1b., or other appropriate packaging materials in 3.0, must be used. Void spaces within multiple book containers must be filled with dunnage or otherwise stabilized to prevent shifting or damage to the contents or container. Shipments of books and similarly produced printed matter are packaged according to these weight categories: a. Up to five pounds, sealing must be by multiple friction closures, completely clinched staples, heat-sealing, adhesives, tape, or nonmetallic banding. Although shrinkwrap is not acceptable as the only packaging for hardback books and similarly produced printed matter exceeding one pound or one inch thick, it may be used on the exterior of otherwise acceptable containers. Shrinkwrap (under 3.6) may be used as the only method of packaging for paperback books and similarly produced printed matter up to three pounds. b. From 5 to 10 pounds, closure must be by tape, nonmetallic banding, or adhesives. Reinforced tape or nonmetallic banding is adequate for both closure and reinforcement. Nonmetallic banding must be firmly applied to the point that the straps must be tightened until they depress the carton at the edges. c. From 10 to 25 pounds, reinforced tape or nonmetallic banding is adequate for closure and reinforcement. Nonmetallic banding must be firmly applied to the point that the straps tighten until they depress the carton at the edges. d. From 25 to 50 pounds, hardbound books and similarly produced printed matter must be packaged in 275-pound test fiberboard boxes and paperback books and similarly produced printed matter must be packaged in 200-pound test fiberboard boxes. e. From 50 to 70 pounds, hardbound books and similarly produced printed matter must be packaged in 350-pound test fiberboard boxes and paperback books and similarly produced printed matter must be packaged in 275-pound test fiberboard boxes. 7.3 Soft GoodsBoxes containing soft goods (e.g., textiles, clothing, sheets, blankets, pillows and pillowcases, draperies, cloth, and any wearing apparel) weighing up to 5 pounds must be filled to capacity. Soft goods between the weight range of 5 to 20 pounds must be packaged in material with a minimum 70-pound outer ply basis weight. Closure of bags must be by completely clinched staples, heat-sealing, adhesives, sewing, or tape. Improperly clinched staples must be removed. Shrinkwrapping is not acceptable as the only packaging. Fiberboard containers must be made of at least 200-pound test board for soft goods weighing from 20 to 45 pounds and at least 275-pound test board for soft goods weighing from 45 to 70 pounds. 7.4 Sound RecordingsShipments of recordings (e.g., records and cassette tapes in paper sleeves, paperboard, or chipboard shells) weighing up to 10 pounds must be packed in 70-pound basis weight envelopes for weights up to 3 pounds, or outer corrugated, fiberboard containers for weights up to 10 pounds. When shipments weigh from 20 to 40 pounds, multiple shell containers must be packaged in 175-pound test fiberboard containers or equivalent and closed and reinforced by adhesives, kraft paper tape, equivalent plastic tape, or staples. When shipments weigh from 40 to 65 pounds, multiple shell containers up to 65 pounds must be packaged in 200-pound test fiberboard containers or equivalent and closed and reinforced as described for 20- to 40-pound containers, except that containers must be reinforced about every 8 inches around the package. Shipments weighing more than 65 pounds must be packaged in 275-pound test fiberboard containers or equivalent. 7.5 Magnetic TapesShipments of multiple magnetic tapes and cartridges up to 5 pounds must be packed in outer fiberboard containers or chipboard containers (minimum 0.022 mil). Closure must be by multiple friction closures, completely clinched staples, heat-shrinking or adhesives, or by tape. Paper tape must be a minimum of 60-pound basis weight kraft. Shrinkwrapping is acceptable on the exterior of otherwise acceptable boxes of multiple tape shipments. Standards for shipments weighing from 5 to 20 pounds are similar, except that closure must be only by the use of adhesives, tape, or staples. Standards are also similar for shipments weighing from 20 to 40 pounds, except that the contents must be placed in 175-pound test containers that are banded or reinforced at two points with reinforced paper or plastic tape, pressure-sensitive filament tape, or firmly applied nonmetallic banding. Shipments from 40 to 65 pounds must be similarly packaged, except that fiberboard containers of at least 200-pound test board or equivalent must be used. Shipments weighing more than 65 pounds must be packaged in 275-pound test fiberboard containers or equivalent. 8.0 Nonmailable and Restricted Articles and Substances Generally8.1 Nonmailable Matter—GeneralCertain potentially undesirable, harmful, or dangerous matter is nonmailable by statute or regulation. The standards for nonmailable articles and substances and the special conditions under which certain of these articles and substances may be mailed are in 8.0 through 10.0 and 12.0. The standards in 13.0, Written, Printed, and Graphic Matter Generally, 508.9.0, Pandering Advertisements, and 508.10.0, Sexually Oriented Advertisements, apply to nonmailable matter in written, printed, or graphic form and contain the rules on advising mailers of matter covered in 8.0 through 13.0, 508.9.0, and 508.10.0. The standards in 8.0 through 10.0 and 12.0 apply to the military postal system, its employees, and undelivered mail that is or has been in the official custody of this system and its employees. References to Inspection Service apply to the Postal Inspection Service and authorized employees, not military investigative services. 8.2 Basic PremiseThe basic premise of the postal mailability statutes is that anything “which may kill or injure another, or injure the mails or other property...” is nonmailable. Several statutory exceptions to this rule permit mailings of otherwise nonmailable matter under specified conditions. Statutory exceptions apply to live scorpions, poisonous drugs and medicines, poisons for scientific use, switchblade knives, firearms, motor vehicle master keys, locksmithing devices, and abortive and contraceptive devices. The statutes also provide that the USPS may, by regulation, permit the mailing, under required conditions of preparation and packing, of potentially harmful matter not “outwardly or of [its] own force dangerous or injurious to life, health, or property.” The standards in 8.0 summarize the statutory prohibitions and exceptions. The mailability standards that apply to perishable, hazardous, and restricted matter are detailed in 9.0, 10.0, and 12.0, respectively. Publication 52, Hazardous, Restricted, and Perishable Mail, contains additional clarification and further describes the conditions of preparation and packaging under which the USPS accepts for mailing potentially harmful matter that is otherwise nonmailable. Publication 52 also contains detailed information on the mailability of specific hazardous materials. 8.3 Other Nonmailable MatterMatter is nonmailable also when it cannot be delivered because of an illegible, incorrect, or insufficient address, or when it does not meet USPS standards for mail preparation, classification, postage prices, size, or weight. 8.4 Restricted Matter—GeneralRestricted matter is an article or substance prohibited or limited by Title 18, U.S. Code (liquors, abortive and contraceptive devices, odd-shaped items in envelopes, motor vehicle master keys, and locksmithing devices). It also includes matter not otherwise described in 8.0 through 10.0 and 12.0 that is restricted by 18 USC 1716(a) because it may, under conditions encountered in the mail, be injurious to life, health, or property (obnoxious odors, liquids, powders, and battery-powered devices). 8.5 Harmful Matter—GeneralExcept as provided in this document, any article, composition, or material is nonmailable if it can kill or injure another or injure the mail or other property. Harmful matter includes, but is not limited to: a. All types and classes of poisons, including controlled substances. b. All poisonous animals except scorpions mailed for medical research purposes or for the manufacture of antivenom; all poisonous insects; all poisonous reptiles; and all types of snakes, turtles, and spiders. c. All disease germs or scabs. d. All explosives, flammable material, infernal machines, and mechanical, chemical, or other devices or compositions that may ignite or explode. 8.6 Hazardous MaterialsHarmful matter also includes regulated hazardous materials as defined in 10.0 that are likely to harm USPS employees or to destroy, deface, or otherwise damage mail or postal equipment. This includes materials such as caustic poisons (acids and alkalies), oxidizers, or highly flammable liquids, gases, or solids; or materials that are likely, under conditions incident to transportation, to cause fires through friction, absorption of moisture, or spontaneous chemical changes or from retained heat from manufacturing or processing, including explosives or containers previously used for shipping high explosives with a liquid ingredient (such as dynamite), ammunition, fireworks, radioactive materials, matches, or articles emitting obnoxious odors. 8.7 Marking of Restricted Articles or Substances8.7.1 ContentExcept for firearms and switchblade knives, controlled substances, radioactive materials, and motor vehicle master keys and locksmithing devices, the identity of the content of anything mailed under 8.0 through 10.0 and 12.0 must be plainly and durably marked on the address side of each mailpiece as a condition of mailing. When the content is a hazardous material as defined in 49 CFR, each mailpiece must be marked as required in 10.0. 8.7.2 AddressingFor any matter mailed under the provisions in 8.0 through 10.0 and 12.0, the recipient’s name and address must be affixed or applied directly to the mailpiece using a material or method that is not water-soluble and not easily smeared or rubbed off. Except for diagnostic specimen mailpieces using a business reply mail format and nonregulated materials, a return address that includes the sender’s name and address must appear on all matter mailed under 8.0 through 10.0 and 12.0. The return address, when required, must be applied using a material or method that is not water-soluble and not easily smeared or rubbed off. 8.7.3 Warning LabelExcept for controlled substances mailed under 12.0, any label or other marking required by federal law or the regulation of any federal agency must be securely affixed or applied to the address side of each mailpiece. See 10.0 for the warning label requirements that apply to the mailing of hazardous materials. 8.8 Mailer ResponsibilityThe mailer must comply with applicable postal laws and regulations governing mailability and preparation for mailing, as well as nonpostal laws and regulations on the shipment of particular matter. 8.9 Statutory System18 USC 2510, et seq., constitutes a statutory system of regulating interception of wire, oral, or electronic communications. Any person contemplating the mailing of a device primarily useful for surreptitiously effecting such interception should consider the provisions of 18 USC 2510, et seq., particularly section 2512. This statute makes it a crime, except as otherwise provided in 18 USC 2510, et seq., for a person intentionally to send through the mail any device whose design that person knows, or has reason to know, renders the device primarily useful for surreptitious interception of wire, oral, or electronic communications. The statute does not declare that such a device in itself constitutes nonmailable matter but, as indicated, provides criminal penalties for the act of intentionally mailing it. 8.10 Other Laws and RegulationsParticular matter may be mailable under postal statutes and regulations, but customers may have responsibilities under nonpostal statutes and regulations concerned with possession, treatment, transmission, or transfer of such matter (e.g., 49 CFR 100-185 (Department of Transportation Regulations); the Comprehensive Drug Abuse Prevention and Control Act of 1970 (Public Law 91-513), 21 USC 801, et seq.; and the Gun Control Act of 1968 (Public Law 90-618), 18 USC 921, et seq.). 8.11 Refusal of Nonmailable MatterUSPS employees may refuse an article for mailing if the content of the article is described by the mailer or otherwise revealed to be nonmailable. 8.12 Authorizing MailabilityA postmaster may decide whether articles and substances other than written, printed, or graphic matter are nonmailable and, where appropriate, is authorized to refuse to accept for mailing such matter determined to be nonmailable. The mailer may seek a review of the postmaster’s decision by the PCSC. The mailer may file a written appeal of the PCSC ruling with the USPS Recorder, Judicial Officer, with a copy or description of the determination or ruling. The rules of procedure for the determination of such appeals are in 39 CFR 953. 8.13 Protecting EmployeesA postmaster may take any step reasonable and necessary to protect USPS employees and equipment from potentially dangerous or injurious materials or substances found in the mail. 8.14 Applicability to Military Postal System8.0 through 10.0 and 12.0 applies to the military postal system, its personnel, and undelivered mail that is or has been in the official custody of that system and its personnel. References to the Inspection Service refer to the Postal Inspection Service and its authorized employees, not to military investigative services. 9.0 Perishables9.1 Time FactorMailable perishable matter may be sent through the mail only if it can reach its destination in good condition in the normal transit time between the mailing and address points. Mailable perishable foods that do not rapidly decay or generate obnoxious odors in the mail may be sent at the mailer’s risk. 9.2 Preparation of Perishables9.2.1 ContainerAny container used to mail perishable matter must be constructed to protect and securely contain the contents. 9.2.2 ProduceFruits and vegetables are not mailable unless presented in dry condition. 9.2.3 Water IceWater ice used as a refrigerant must be packed under 2.4 as though it were a liquid. 9.2.4 Dry IceA parcel containing dry ice (carbon dioxide solid) must be packed in a container that allows the release of carbon dioxide gas. If a fiberboard box is used, enough insulation is necessary to prevent condensation and wetting of the mailing carton. 9.3 Live Animals9.3.1 Prohibition on Animals Intended for Use in an Animal Fighting VentureAn animal is nonmailable if such animal is being mailed for the purpose of having it participate in an animal fighting venture (7 U.S.C. 2156). This standard applies regardless of whether such venture is permitted under the laws of the state in which it is conducted. Violators can be subject to the criminal penalties in 18 U.S.C. 49. See 12.20 for the prohibition on mailing sharp instruments intended for use in an animal fighting venture and 13.5.7 for restrictions on mailing written, printed, or graphic matter related to animal fighting ventures. For this standard: a. the term animal means any live bird, or any live mammal (e.g., dog), except human; b. the term animal fighting venture means any event, in or affecting interstate or foreign commerce, that involves a fight conducted or to be conducted between at least two animals for purposes of sport, wagering, or entertainment (excluding any activity whose primary purpose involves using one or more animals in hunting other animals); and c. the term state means any state of the United States, the District of Columbia, the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico, or any U.S. territory or possession. 9.3.2 Day-Old PoultryDay-old poultry vaccinated with Newcastle disease (live virus) is nonmailable. Live day-old chickens, ducks, emus, geese, guinea fowl, partridges, pheasants (pheasants may be mailed only from April through August), quail, and turkeys are acceptable in the mail only if: a. They are not more than 24 hours old and are presented for mailing in the original unopened hatchery box from the hatchery of origin. b. The date and hour of hatching is noted on the box by a representative of the hatchery who has personal knowledge thereof. (For COD shipments made by a hatchery for the account of others, the name or initials and address of the hatchery or the Post Office box number and address of the hatchery must be prominently shown for this standard.) c. The box is properly ventilated, of proper construction and strength to bear safe transmission in the mail, and not stacked more than 10 units high. d. They are mailed early enough in the week to avoid receipt at the office of address, in case of missed connections, on a Sunday, on a national holiday, or on the afternoon before a Sunday or holiday. e. They can be delivered to the addressee within 72 hours of the time of hatching, whether the addressee resides in town or on a rural route or highway contract route. f. The shipment bears special handling postage in addition to regular postage, unless sent at the First-Class Mail or Priority Mail prices. g. When live, day-old poultry is to be transported by aircraft, all provisions of the airline tariffs are met and air carriers have equipment available to safely deliver shipments within the specified time limits, allowing for delays en route in air and ground transportation. h. Day-old poultry, originally shipped by air express or air cargo and then presented for mailing, must be in good condition and prepared as specified in 9.3.2a. through 9.3.2e. i. Boxes of day-old poultry of about identical size, securely fastened together to prevent separation in transit, may be accepted for mailing as a single parcel, if such parcel is not more than 100 inches in length and girth combined. 9.3.3 Small Cold-Blooded AnimalsSmall, harmless, cold-blooded animals (except snakes and turtles) that do not require food or water or attention during handling in the mail and that do not create sanitary problems or obnoxious odors are mailable (e.g., baby alligators and caimans not more than 20 inches long, bloodworms, earthworms, mealworms, salamanders, leeches, lizards, snails, and tadpoles). 9.3.4 Adult FowlDisease-free adult fowl may be mailed domestically when shipped under applicable law in accordance with 1.7. Adult chickens, turkeys, guinea fowl, doves, pigeons, pheasants, partridges, and quail as well as ducks, geese, and swans are mailable as follows: a. The mailer must send adult fowl by Express Mail in secure containers approved by the manager, Product Classification (see 608.8.0 for address). b. The number of birds per parcel must follow the container manufacturer limits and each bird must weigh more than 6 ounces. c. A mailing container must be used that is constructed by a USPS-approved manufacturer listed on the RIBBS website at http://ribbs.usps.gov. d. Indemnity may be paid only for articles that are lost, damaged, or missing contents, and not for death of the birds in transit if there is no visible damage to the mailing container. e. Postage refunds may not be available if the Express Mail shipment was delivered or delivery was attempted within three days of the date of mailing as shown in the “Date In” box on Label 11. 9.3.5 Warm-Blooded AnimalsWarm-blooded animals, except the specified birds under specific conditions in this section, are not mailable (e.g., hamsters, mice, rats, guinea pigs, rabbits, cats, dogs, squirrels, parakeets, and canaries). 9.3.6 Mailed to the Pacific IslandsAnimals mailed to the Republic of Palau, the Republic of the Marshall Islands, and the Federated States of Micronesia require a permit issued by the government of the destination country. 9.3.7 BeesBees are acceptable in the continental surface mail when shipped under federal and state regulations to ensure that they are free of disease. Packages of honeybees must bear special handling postage, except those sent at a First-Class Mail price. Only queen honeybees may be shipped via air transportation. Each queen honeybee shipped via air transportation may be accompanied by up to eight attendant honeybees. 9.3.8 Other InsectsOther live, nonpoisonous, and nondisease-conveying insects, including flies of the family Drosophilidae, may be sent through the mail when properly prepared for mailing and when shipped under regulations of the U.S. Department of Agriculture. Such insects mailed to the Republic of Palau, the Republic of the Marshall Islands, and the Federated States of Micronesia are also subject to the regulations of the destination country. 9.3.9 Live ScorpionsLive scorpions that are to be used for medical research or the manufacture of antivenin are accepted only in the continental surface mail when packaged in a double mailing container, both parts of which are closed or fastened to prevent escape of the scorpions. The inner container must be of material that cannot be punctured by the scorpions and must be plainly marked “Live Scorpions.” Cushioning material must be used when necessary to prevent shifting of the inner container. The outer container must be strong enough to prevent crushing of the package or exposure of the contents during normal handling in the mail. The outer container must be plainly marked “Live Scorpions.” 9.3.10 PackagingAny mailing container used for mailable animals must be made of at least 275-pound test, double wall, corrugated, weather-resistant fiberboard (W5c) or equivalent and must be adequately ventilated. The container must be constructed to prevent escape of the animals while in the mail and to preclude the container and its contents from being crushed in normal handling. The outside of the container must include a return address and a description of the contents. A container marked “If Undeliverable, Abandon” is not accepted. 9.3.11 AcceptanceThe USPS does not accept any shipment of animals that the USPS reasonably believes cannot reach its destination in a viable condition. Such a determination is based on factors including the expected temperatures (weather conditions) while the shipment is in the mail; the types of vehicles on which the shipment is to be transported; the expected transit time; and the types of packaging used for protection against suffocation, crushing, and handling. 9.3.12 DisposalAny parcel of live animals that cannot be delivered to the addressee or returned to the sender within 72 hours (for live day-old poultry) or within the delivery period marked on the parcel (for other animals) is immediately disposed of under the relevant standards. A parcel not marked with the delivery period is disposed of immediately if it reasonably appears that the animals cannot be returned to the sender in a viable condition. 9.4 Dead Wild AnimalsThe dead bodies, or parts thereof, of any wild animals, wild birds, or eggs are acceptable for mailing only when they are lawfully killed or taken, and their shipment is not prohibited by law of the United States or of the state, territory, district, or foreign country or subdivision thereof in which killed or taken or offered for shipment. Mailing of fresh game is also subject to these standards. 9.5 Furs, Hides, Skins, And PeltsA parcel containing the fur, hide, skin, or pelt of a wild animal is mailable only if the matter is properly dried or cured and has no offensive odor, and only if the parcel is plainly marked, labeled, or tagged on the outside with the names and addresses of the shipper and addressee. The parcel must bear any endorsement required by state laws. Hides and pelts must be wrapped when necessary to prevent damage to other mail. 9.6 Mailing Plants9.6.1 MailabilityIn general, plants and plant products are mailable within the United States and its territories and possessions, subject to certain prohibitions imposed under U.S. agriculture and conservation statutes. To the extent specified below, when such prohibitions make shipment of plants or plant products unlawful, those articles constitute nonmailable matter. More detailed information is in Publication 14, Prohibitions and Restrictions on Mailing Animals, Plants, and Related Matter. 9.6.2 Nonmailable Quarantined MatterUnder 39 USC 3014(b), any plant, plant product, or other article capable of carrying a dangerous plant disease or insect infestation is nonmailable from a quarantined area, if shipping such item by common carrier is prohibited by a U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) quarantine issued under 7 USC 161, except, any such item is mailable from a quarantined area if: a. Its movement by common carrier is allowed under conditions prescribed in the quarantine notice or in other USDA regulations, issued under 7 USC 161, governing its inspection, disinfection, certification, and other conditions for its movement. b. Its movement by mail complies with all such conditions. 9.6.3 Additional Quarantined MatterAny plant, article, or matter, the importation or interstate shipment of which is prohibited under the Act of August 20, 1912 (37 Stat. 315, chapter 308; 7 USC 151 et seq.), commonly known as the Plant Quarantine Act, is made nonmailable by 39 USC 3015(c). 9.6.4 Illegally Taken PlantsAny plant, the conveyance of which is prohibited under section 3 of the Lacey Act Amendments of 1981 (16 USC 3372), is made nonmailable by 39 USC 3015(d). 9.6.5 Criminal Penalties18 USC 1716B provides criminal penalties for mailing anything nonmailable under 39 USC 3014(b), unless the item is excepted under USPS regulations. 18 USC 1716D provides criminal penalties for mailing anything nonmailable under 39 USC 3015(c) and (d). 9.6.6 USDA Notices and RegulationsUSDA quarantine notices, issued under 7 USC 161, are published in the Federal Register and codified in 7 CFR (e.g., 7 CFR 301 and 318). Details on these and other USDA regulations may be obtained by writing to the USDA Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service (APHIS) Plant Protection and Quarantine (PPQ) Programs (see 608.8.0 for address). 9.7 Nonmailable Plant Pests, Injurious Animals, and Illegally Taken Fish or Wildlife9.7.1 Nonmailable MatterMore detailed information is in Publication 14. Under the respective provisions of 39 USC 3015(a), (b), and (d), the following items are nonmailable: a. Any injurious animal, the importation or interstate shipment of which is prohibited under 18 USC 42. b. Any plant pest, the movement of which is prohibited under section 103 or 104 of the Federal Plant Pest Act (7 USC 150bb or 150cc). c. Any fish or wildlife, the conveyance of which is prohibited under section 3 of the Lacey Act Amendments of 1981 (16 USC 3372). 9.7.2 Criminal Penalties18 USC 1716D provides criminal penalties for mailing anything nonmailable under 39 USC 3015(a), (b), or (d). 10.0 Hazardous Materials10.1 DefinitionsThe following definitions apply: a. Hazardous material is any article or substance designated by the U.S. Department of Transportation (DOT) as being capable of posing an unreasonable risk to health, safety, and property during transportation. In international commerce, hazardous materials are known as “dangerous goods.” b. Limited quantity is the maximum amount of a specific hazardous material that is exempted from the labeling or packaging requirements in 49 CFR. Not every hazardous material is eligible to be shipped as a limited quantity. Almost all limited quantity materials are nonmailable. c. ORM-D (Other Regulated Material) material is a limited quantity of a hazardous material that presents a limited hazard during transportation due to its form, quantity, and packaging. In almost all instances, the proper shipping name for an ORM-D material is consumer commodity. Not all hazardous material permitted to be shipped as a limited quantity can qualify as an ORM-D material. ORM-D materials having the proper shipping name of “consumer commodity” are mailable subject to USPS quantity and packaging standards. d. Consumer commodity is a hazardous material that is packaged and distributed in a quantity and form intended or suitable for retail sale and designed for consumption by individuals for their personal care or household use purposes. This term can also include certain drugs or medicines. Not all hazardous material permitted to be shipped as a limited quantity can qualify as a consumer commodity. e. Air transportation requirements, for the purposes of 10.0 only, apply to all mailable hazardous materials sent at the First-Class Mail, Priority Mail, or Express Mail prices. All mailable hazardous materials sent at those prices must meet the requirements that apply to air transportation. Mailable hazardous materials sent at any of those prices may or may not be transported via air depending on the distance between the point of origination and the point of destination, and the ability of the USPS to obtain an air carrier between those points. f. Surface transportation requirements, for the purposes of 10.0 only, apply to all mailable hazardous materials sent at the Standard Mail or Package Services prices. All mailable hazardous materials sent at the Standard Mail or Package Services prices must meet the requirements that apply to surface transportation. g. Primary receptacle is the container (e.g., tube, vial, bottle) that holds the hazardous material. h. Secondary container is the packaging component into which the primary receptacle(s) and any required absorbent and cushioning material is securely placed. The packaging of certain mailable hazardous materials does not require the use of a secondary container. i. Outer shipping container is the exterior packaging component into which a primary receptacle, along with any required absorbent and cushioning material, and the secondary container (if required) are securely placed. The outer shipping container bears the addressing information along with all required markings. 10.2 U.S. Department of Transportation Regulations of Hazardous MaterialThe U.S. Department of Transportation (DOT) regulates the surface and air carriage of hazardous materials within the United States via any means of transportation. The DOT regulations for the transport of hazardous materials are codified in Title 49, Code of Federal Regulations (49 CFR) 100–185. USPS mailing standards for hazardous materials generally adhere to 49 CFR, but also include many additional limitations and prohibitions. 10.3 USPS Standards for Hazardous MaterialThe USPS standards generally restrict the mailing of hazardous materials to ORM-D materials with the proper shipping name of “consumer commodity” that meet USPS quantity limitations and packaging requirements. The few non-ORM-D materials permitted to be mailed are subject to the standards in 10.0. Detailed information on the mailability of specific hazardous materials is contained in Publication 52, Hazardous, Restricted, and Perishable Mail. 10.4 Hazard ClassEvery hazardous material is assigned to one of nine hazard classes identified in 49 CFR 172.101 and 173. Some hazard classes are further separated into divisions based on their physical or chemical properties. For postal purposes, Exhibit 10.4 generally summarizes the mailability of hazardous materials by hazard class. Exhibit 10.4 DOT Hazard Classes and Mailability Summary 10.5 Mailer Responsibility for Mailing Hazardous MaterialsFull responsibility rests with the mailer to comply with all postal and nonpostal laws and regulations regarding the mailing of hazardous materials. Anyone who mails, or causes to be mailed, a nonmailable or improperly packaged hazardous material can be subject to legal penalties, including but not limited to those specified in 18 USC. 10.6 Mailability Rulings for Hazardous MaterialsGenerally, the acceptability for mailing chemicals and other types of hazardous materials depends on container fluid/vapor capacities, the ability of the complete mailpiece to contain the material, and the method of absorbing and containing the product in case of accidental leakage of the primary receptacle. To determine mailability of a specific material, a mailer must submit a material safety data sheet (MSDS) and the following information to the Pricing and Classification Service Center (PCSC): a. Name of material, hazard class, and assigned United Nations (UN) or North America (NA) identification number. b. Chemical composition by percentage of ingredient. c. Flashpoint. e. Irritant action when inhaled, swallowed, or contacted by eyes or skin. f. Special precautions necessary to permit handling without harm to USPS employees or damage to property or other mail. g. Explanation of warning labels and shipping papers required by state or federal regulations. h. Proposed packaging method, including the addressing and required markings. i. Proposed number of pieces to be mailed, class of mail, and Post Office(s) of mailing. 10.7 Warning Labels for Hazardous MaterialsWith few exceptions as noted in these standards, most hazardous materials acceptable for mailing fall within the Other Regulated Materials (ORM-D) regulations of CFR 49 173.144, which do not require DOT hazard class warning labels. Except for Division 6.2 materials under 10.17.4 and dry ice under 10.20.4, any hazardous material bearing or required to bear a DOT hazard class warning label under the requirements in 49 CFR is prohibited from mailing. Mailable ORM-D material must be marked as required in 10.8. Mailable hazardous material must bear DOT handling labels (e.g., orientation arrows, magnetized materials) when applicable. 10.8 Package Markings for Hazardous MaterialsEach mailpiece containing a mailable hazardous material must be plainly and durably marked on the address side with the required shipping name and UN identification number. The UN identification number is not required on a mailpiece that contains an ORM-D material. A mailable ORM-D material must be marked on the address side with “ORM-D” or “ORM-D AIR,” as applicable, immediately following or below the proper shipping name. The proper shipping name for a mailable ORM-D material is “consumer commodity.” The designation “ORM-D” or “ORM-D AIR”, as required, must be placed within a rectangle that is approximately 6.3 mm (1/4 inch) larger on each side than the designation. Mailable ORM-D materials sent as Standard Mail or Package Services must also be marked on the address side as “Surface Only” or “Surface Mail Only.” 10.9 Shipping Papers for Hazardous MaterialsA shipper’s declaration for dangerous goods (shipping paper) prepared under 49 CFR 172.200 through 172.205 is required for certain types of hazardous materials when mailed. The shipping paper must be completed and signed in triplicate by the mailer. It must be affixed to the outside of the mailpiece within an envelope or similar carrier that can be easily opened and resealed to allow viewing of the document. Shipping papers are required as follows: a. Air transportation requirements. Except for nonregulated materials sent under 10.17.3 or 10.17.8 and diagnostic specimens sent under 10.17.5, mailpieces containing mailable hazardous materials sent at the First-Class Mail, Priority Mail, or Express Mail prices must include a shipping paper. b. Surface transportation requirements. Except for nonregulated materials sent under 10.17.3 or 10.17.8 and mailable ORM-D materials, mailpieces containing mailable hazardous materials sent at the Standard Mail or Package Services prices must include a shipping paper. 10.10 Air Transportation Prohibitions for Hazardous MaterialsAll mailable hazardous materials sent at the First-Class Mail, Priority Mail, or Express Mail prices must meet the requirements for air transportation. The following types of hazardous materials that are prohibited from carriage on air transportation must not be sent at the First-Class Mail, Priority Mail, or Express Mail prices: a. Anything susceptible to damage or that can become harmful because of changes in temperature or atmospheric pressures unless protected against the effects of such changes. b. Magnetic materials that have a field strength sufficient to cause a compass deviation at a distance of 15 feet (4.6 meters) or more from any point on the outer packaging. c. Flammable materials (gases, liquids, and solids). e. Materials excluded from air shipment by DOT regulations (49 CFR 100-185) or of the applicable state (country) or air carrier operator variations. Certain restricted articles, as described in 49 CFR 100-185 and the operator variations of the air carriers, may be accepted for air transportation if properly packaged. These articles must be labeled and bear a shipper's declaration in triplicate, as required by 49 CFR 172.204, or must be marked according to the air carrier's operator variations. Refer to the technical instruction of the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) for air carrier operator variations. 10.11 Explosives (Hazard Class 1)10.11.1 DefinitionAn explosive is any substance, article, or device that is designed to function by explosion (i.e., an extremely rapid release of gas and heat) or that, by chemical reaction within itself, is able to function in a similar manner even if not designed to function by explosion, unless the substance or article is otherwise classed under the provisions in 49 CFR. Hazard class 1 has six divisions as shown in Exhibit 10.4. No further explanation of the six divisions is provided in these standards because explosives are prohibited in the mail except as permitted in 10.11.2. 10.11.2 MailabilityExplosives are prohibited in international mail. Explosives are prohibited in the domestic mail via air transportation. For domestic surface transportation, explosives are prohibited except for certain Division 1.4S toy propellant devices and safety fuses specifically approved by the manager, Product Classification (see 608.8.0 for address) before mailing. A mailable explosive must meet the packaging and marking requirements provided with the manager’s approval. A shipping paper is required. 10.12 Gases (Hazard Class 2)10.12.1 DefinitionHazard class 2 consists of three divisions: a. Division 2.1, Flammable Gases. A material that is a gas at 68°F (20°C) or less and 14.7 psi (101.3 kPa) of pressure. Flammable gases also include materials that have a boiling point of 68°F (20°C) or less at 14.7 psi (101.3 kPa) and that are ignitable at 14.7 psi (101.3 kPa) when in a mixture of 13% or less by volume with air or that have a flammable range at 14.7 psi (101.3 kPa) with air of at least 12% regardless of the lower limit. These conditions must be established in accordance with ASTM E681-85, Standard Test Method for Concentration Limits of Flammability of Chemicals, or other approved equivalent method. The flammability of aerosols must be determined using the tests specified in 49 CFR 173.306(i). b. Division 2.2, Nonflammable, Nontoxic Gases. A material that does not meet the definition of Division 2.1 or 2.3 and exerts in its packaging an absolute pressure of 40.6 psi (280 kPa) or greater at 68°F (20°C). c. Division 2.3, Toxic Gases. A material that is poisonous by inhalation and is a gas at 68°F (20°C) or less and a pressure of 14.7 psi (101.3 kPa) or a material that has a boiling point of 68°F (20°C) or less at 14.7 psi (101.3 kPa). 10.12.2 MailabilityGases are prohibited in international mail. Toxic gases in Division 2.3 are prohibited in domestic mail. Flammable gases in Division 2.1 are prohibited in domestic mail via air transportation, but are permitted via surface transportation if the material can qualify as an ORM-D material and meet the standards in 10.12.3 and 10.12.4. Nonflammable gases in Division 2.2 are generally permitted in the domestic mail via air or surface transportation if the material can qualify as an ORM-D material and meet the standards in 10.12.3 and 10.12.4. 10.12.3 ContainerAn other-than-metal primary receptacle containing a mailable gas may be acceptable if the water capacity of the primary receptacle is 4 fluid ounces (7.22 cubic inches) or less per mailpiece and the primary receptacle meets 49 CFR requirements. Mailable nonflammable and flammable compressed gases are acceptable in metal primary receptacles that have a water capacity up to 33.8 fluid ounces (1 liter or 61.0 cubic inches), depending on their internal pressure. A DOT 2P container must be used as the primary receptacle if the internal pressure is from 140 to 160 psi at 130°F (55°C). A DOT 2Q container must be used as the primary receptacle if the pressure is from 161 to 180 psi at 130°F (55°C). A container with an internal pressure over 180 psi at 130°F (55°C) is prohibited from mailing. Mailable flammable compressed gases are restricted to 33.8 fluid ounces (1 liter) per mailpiece. Mailable nonflammable compressed gases are permitted in individual 33.8 fluid ounce (1 liter) containers that must be securely packed within an outer shipping container. Each mailpiece must not exceed a total weight of 25 pounds. 10.12.4 MarkingFor surface transportation, packages of mailable gases must be clearly marked on the address side with “Surface Only” or “Surface Mail Only” and “ORM-D” immediately following or below the proper shipping name (consumer commodity). For air transportation, packages must be plainly and durably marked on the address side with “ORM-D AIR” immediately following or below the proper shipping name and must also bear a shipper's declaration for dangerous goods. 10.13 Flammable and Combustible Liquids (Hazard Class 3)10.13.1 DefinitionsThe terms used in the standards that apply to hazard class 3 are defined as follows: a. Flammable liquid means a liquid that has a flashpoint of not more than 141°F (60.5°C), or any material in a liquid phase that has a flashpoint at or above 100°F (38°C). b. Combustible liquid means any liquid that does not meet the definition of any other hazard class and has a flashpoint above 141°F (60.5°C) and below 200°F (93°C). Note: A flammable liquid with a flashpoint at or above 100°F (38°C) that does not meet the definition of any other hazard class may be reclassified as a combustible liquid per 49 CFR 173.120(b). 10.13.2 Flammable Liquid MailabilityFlammable liquid is prohibited in international mail. Flammable liquid with a flashpoint of 20°F (-7°C) or below is prohibited in domestic mail. Other flammable liquid is prohibited in domestic mail via air transportation but is permitted via surface transportation if the material can qualify as an ORM-D material and meet the following conditions as applicable: a. The flashpoint is above 20°F (-7°C) but no more than 73°F (23°C); the liquid is in a metal primary receptacle not exceeding 1 quart, or in another type of primary receptacle not exceeding 1 pint, per mailpiece; enough cushioning surrounds the primary receptacle to absorb all potential leakage; the cushioning and primary receptacle are packed within a securely sealed secondary container that is placed within a strong outer shipping container; and each mailpiece is plainly and durably marked on the address side with “Surface Only” or “Surface Mail Only” and “ORM-D” immediately following or below the proper shipping name. b. The flashpoint is above 73°F (23°C) but less than 100°F (38°C); the liquid is in a metal primary receptacle not exceeding 1 gallon, or in another type of primary receptacle not exceeding 1 quart, per mailpiece; enough cushioning surrounds the primary receptacle to absorb all potential leakage; the cushioning and primary receptacle are placed within a securely sealed secondary container that is placed within a strong outer shipping container; and each mailpiece is plainly and durably marked on the address side with “Surface Only” or “Surface Mail Only” and “ORM-D” immediately following or below the proper shipping name. 10.13.3 Combustible Liquid MailabilityCombustible liquid is prohibited in international mail. Combustible liquid is permitted in domestic mail if the material can qualify as an ORM-D material and meet the following conditions as applicable: a. For surface transportation, if the flashpoint is 100°F (38°C) but no more than 141°F (60.5°C); the liquid is in a metal primary receptacle not exceeding 1 gallon, or in another type of primary receptacle not exceeding 1 quart, per mailpiece; enough cushioning surrounds the primary receptacle to absorb all potential leakage; the cushioning and primary receptacle are packed in a securely sealed secondary container that is placed within a strong outer shipping container; and each mailpiece is plainly and durably marked on the address side with “Surface Only” or “Surface Mail Only” and “ORM-D” immediately following or below the proper shipping name. b. For surface or air transportation, if the flashpoint is above 141°F (60.5°C) but no more than 200°F (93°C); the liquid is in a primary receptacle not exceeding 1 gallon per mailpiece; enough cushioning surrounds the primary receptacle to absorb all potential leakage; the cushioning and primary receptacle are packed in a securely sealed secondary container that is placed within a strong outer shipping container; and each mailpiece is plainly and durably marked on the address side with “ORM-D” or “ORM-D AIR,” as applicable, immediately following or below the proper shipping name. Mailable material sent via surface transportation must be marked on the address side as “Surface Only” or “Surface Mail Only.” For air transportation, each mailpiece must bear a shipper’s declaration for dangerous goods. c. For air or surface transportation, if the flashpoint is above 200°F (93°C) the material is not regulated as a hazardous material. Such nonregulated materials must be properly and securely packaged to prevent leakage under the general packaging requirements in 2.0, Packaging. 10.13.4 Cigarette LightersA cigarette lighter equipped with an ignition element and containing flammable liquid fuel is a Class 3 flammable liquid. A cigarette lighter that contains a flammable gas is classed as a Division 2.1 flammable gas. A cigarette lighter containing either flammable liquid or flammable gas is permitted only in domestic mail via surface transportation when all of the following conditions are met: a. The design of the lighter is approved by a lighter certification agency authorized by the DOT Associate Administrator for Hazardous Material Safety, per 49 CFR 173.21(i) and 173.308; and an approval number (e.g., “LAA****”) is issued. b. The prospective mailer of the lighter submits to the PCSC manager a written request for authorization to mail the lighter, accompanied by a legible photocopy of the official DOT notice conveying the approval described in 10.13.4a and a specimen of the actual lighter, the packaging materials in which each lighter is to be mailed, the number of mailpieces, and the mailing location. The mailer will receive a written decision from the PCSC manager regarding the requested authorization for mailing. c. When presented for mailing, the address side of the mailpiece containing the lighter must prominently display the approval number, (e.g., “LAA****”), the proper shipping name “Lighter(s)” or “Lighter(s) for Cigarette,” and the marking “Surface Only” or “Surface Mail Only”; all preparation and packaging requirements in the PCSC manager's approval letter have been met; and a legible photocopy of the PCSC manager's approval letter must accompany the mailing. 10.13.5 Special Permit Authorization DOT–SP 9275Manufacturers and distributors seeking to mail parcels via air transportation in accordance with Department of Transportation Special Permit 9275 must submit a written request for approval to the manager, Product Classification (see 608.8.0 for address). Approval to mail parcels using DOT–SP 9275 allows the mailer to use First-Class Mail, Priority Mail, or Parcel Select services for shipping in compliance with all DOT regulations in DOT–SP 9275 and the following mailing requirements: a. Mailers must present a current copy of their DOT Special Permit Authorization letter with a written request for approval to the manager, Product Classification. b. Once approved, mailers must present a copy of their approval letter from the manager, Product Classification (to be kept on file at the office of mailing) at the time of their first mailing at any given postal facility, along with a copy of their current DOT Special Permit Authorization letter. It is the mailers responsibility to provide the office of mailing with updated DOT Special Permit approval letters. The Postal Service may refuse mailings not supported by a current DOT authorization letter. c. Mailers must enter parcels using First-Class Mail, Priority Mail, or Parcel Select service via a USPS-authorized manifest mailing system (MMS) (see 705.2.0). d. Mailers must label each parcel on the address side with “USPS Approved DOT–SP 9275” using at least 14-point type. e. Parcels must weigh 10 pounds or less. Each inner package (receptacle) may not exceed 16 ounces of flammable liquid or 1 pound of solids containing flammable liquid. f. Mailers must ensure that all addressees are notified that they are not authorized to remail the contents of the parcel via the Postal Service under DOT–SP 9275. Mailers must include the following notice: “Flammable substances contained in these packages may be mailed only by consumers (the addressee) via surface transportation in accordance with 10.13. Full responsibility rests with the mailer to comply with all postal and nonpostal statutes and regulations regarding mail. Information regarding postal statutes, regulations, and mailing requirements is available from your local Postmaster or Postal Service Business Mail Entry Manager, and at the Postal Service's mailing standards Web site at pe.usps.com.” g. Mailers must comply with the warning and labeling requirements in 21 CFR Part 700 (740.1 and 701.3) when mailing each parcel. 10.14 Flammable Solids (Hazard Class 4)10.14.1 DefinitionsHazard class 4 consists of three divisions: a. Division 4.1, Flammable Solids. Any solid material other than one classed as an explosive that, under conditions normally incident to transportation, is likely to cause fires through friction or retained heat from manufacturing or processing, or that can be ignited readily and, when ignited, burns so vigorously and persistently as to create a serious transportation hazard. b. Division 4.2, Spontaneously Combustible. A liquid or solid pyrophoric material that even in small amounts and without an external ignition source can ignite within 5 minutes after coming in contact with air, or a self-heating material that, when in contact with air and without an energy supply, is liable to self-heat. c. Division 4.3, Dangerous When Wet. A material that, by contact with water, is likely to become spontaneously flammable or to give off flammable or toxic gas at a price greater than 1 liter per kilogram of the material per hour. 10.14.2 MailabilityFlammable solids are prohibited in international mail. Flammable solids are prohibited in domestic mail via air transportation. A flammable solid that can qualify as an ORM-D material is permitted in domestic mail via surface transportation if the material is contained in a secure primary receptacle having a weight of 1 pound or less; the primary receptacle(s) is packed in a strong outer shipping container with a total weight of 25 pounds or less per mailpiece; and each mailpiece is plainly and durably marked on the address side with “Surface Only” or “Surface Mail Only” and “ORM-D” immediately following or below the proper shipping name. 10.14.3 MatchesMatches are classified as flammable solids. Strike-anywhere matches are prohibited in international and domestic mail. Safety matches (book, card, or strike-on-box) are prohibited in international mail, and in domestic mail via air transportation, but are permitted in domestic mail via surface transportation if: a. They do not ignite spontaneously under conditions normally incident to transportation or when subjected for 8 consecutive hours to a temperature of 200°F (93°C). b. They cannot be readily ignited by friction unless struck on their own or a similar box, card, or book. c. They are tightly packed in a securely sealed primary receptacle to prevent any shifting or movement that could cause accidental ignition by rubbing against adjoining items. The primary receptacle(s) is placed securely within an outer shipping container made of fiberboard, wood, or other equivalent material. Multiple primary receptacles may be placed in a single outer shipping container. The address side of the mailpiece must be marked “Surface Only” or “Surface Mail Only” and “Book Matches,” “Strike-on-Card Matches,” or “Card Matches,” as appropriate. A shipping paper is not required. d. The gross weight of each mailpiece is not more than 25 pounds. 10.15 Oxidizing Substances, Organic Peroxides (Hazard Class 5)10.15.1 DefinitionHazard class 5 consists of two divisions: a. Division 5.1, Oxidizing Substances. A material that may, generally by yielding oxygen, cause or enhance the combustion of other materials. b. Division 5.2, Organic Peroxides. Any organic compound that contains oxygen in the bivalent structure and that may be considered a derivative of hydrogen peroxide, where one or more of the hydrogen atoms have been replaced by organic radicals. 10.15.2 MailabilityOxidizing substances and organic peroxides are prohibited in international mail. For domestic mail, a material that can qualify as an ORM-D material is permitted via air or surface transportation. Liquid materials must be enclosed within a primary receptacle having a capacity of 1 pint or less; the primary receptacle(s) must be surrounded by absorbent cushioning material and held within a leak-resistant secondary container that is packed within a strong outer shipping container. Solid materials must be contained within a primary receptacle having a weight capacity of 1 pound or less; the primary receptacle(s) must be surrounded with cushioning material and packed within a strong outer shipping container. Each mailpiece may not exceed a total weight of 25 pounds. The address side of each mailpiece must be plainly and durably marked with “ORM-D AIR” or “ORM-D,” as applicable, immediately following or below the proper shipping name. A mailable Class 5 material sent via surface transportation must be marked “Surface Mail” or “Surface Mail Only” on the address side. A mailable material sent via air transportation must bear a shipper’s declaration for dangerous goods. 10.16 Toxic Substances (Hazard Class 6, Division 6.1)10.16.1 DefinitionsThe terms used in the standards for Division 6.1 material are: a. Toxic substance is a poisonous material, other than a gas, that is known to be so toxic to humans as to cause death, injury, or harm to human health if swallowed, inhaled, or contacted by the skin. b. Oral toxicity applies to a liquid with a lethal dose (LD50) for acute oral toxicity of not more than 500 mg/kg or a solid with an LD50 for acute oral toxicity of not more than 200 mg/kg that when administered by mouth is likely to cause death within 14 days in half of the test animals. c. Dermal toxicity applies to a material with an LD50 for acute dermal toxicity of not more than 1,000 mg/kg that when administered by continuous contact with bare skin is likely to cause death within 14 days in half of the test animals. d. Inhalation toxicity applies to a dust or mist with a lethal concentration (LC50) for acute inhalation toxicity of not more than 10 mg/L; or a saturated vapor concentration in air at 68°F (20°C) of more than one-fifth of the LC50 for acute toxicity on inhalation of vapors and with an LC50 for acute inhalation toxicity of vapors of not more than 5,000 ml/m3; that when administered by continuous inhalation for 1 hour is likely to cause death within 14 days in half of the test animals. e. Irritating material is any liquid or solid substance (e.g., tear gas) that gives off intense fumes and causes extreme irritation and impairment to a person's ability to function. 10.16.2 MailabilityToxic substances or poisons are prohibited in international mail. For domestic mail, a Division 6.1 toxic substance or poison that can qualify as an ORM-D material is permitted when packaged under the applicable requirements in 10.16.4. Certain other poisonous materials are permitted to be mailed only between the authorized parties and under the conditions in 10.16.3. 10.16.3 Authorized PartiesA Division 6.1 toxic substance having an LD50 for oral toxicity of greater than 5mg/kg but less than or equal to 50 mg/kg is mailable only if packaged under the applicable requirements in 10.16.4 and when sent between authorized parties and under specified conditions, as follows: a. Toxic substances for scientific use (not outwardly or of their own force dangerous or injurious to life, health, or property) may be sent only between manufacturers, dealers, bona fide research or experimental scientific laboratories, and employees of federal, state, or local governments who have official use for such poisons and are designated by the agency head to receive or send such poisons. For air transportation, a shipper’s declaration for dangerous goods is required. b. Poisonous drugs and medicines may be sent only from the manufacturer or dealer of the drugs and medicines to licensed physicians, surgeons, dentists, pharmacists, druggists, cosmetologists, barbers, and veterinarians (18 USC 1716). In limited circumstances, when the mailing is initiated by a drug manufacturer or the drug manufacturer's registered agent, customers may return prescription drugs to the manufacturer or its registered agent as indicated in 12.11.4 and 12.11.5. 10.16.4 Packaging and MarkingThe following requirements must be met, as applicable: a. A toxic substance that can qualify as an ORM-D material and does not exceed a total capacity of 8 ounces per mailpiece is permitted if: the material is held in a primary receptacle(s); enough cushioning material surrounds the primary receptacle to absorb all potential leakage; the cushioning and primary receptacle(s) are packed in another securely sealed secondary container that is placed within a strong outer shipping container. Each mailpiece must be plainly and durably marked on the address side with “ORM-D” or “ORM-D AIR,” as applicable, immediately following or below the proper shipping name. Mailable material sent via surface transportation must be marked on the address side as “Surface Only” or “Surface Mail Only.” b. Other toxic substances and poisons are permitted to be sent between the authorized parties and under the conditions in 10.16.3 when they do not exceed 8 ounces per mailpiece and if: the material is held in a leak-resistant primary receptacle(s); sufficient absorbent and cushioning material completely surround each primary receptacle; the primary receptacle(s) and the absorbent and cushioning materials are firmly held within a leakproof (for liquids) or siftproof (for solids) secondary container; the secondary container is firmly and securely held within a strong outer shipping container of 200-pound grade corrugated fiberboard or equivalent strength. The address side of each mailpiece must be marked with the proper shipping name and UN (or NA) identification number of the material (unless exempted by 12.11.6). Mailable materials sent via surface transportation must be marked on the address side as “Surface Only” or “Surface Mail Only.” Each mailpiece must bear a shipping paper. 10.16.5 IrritantsIrritants are prohibited in international mail and domestic mail. 10.17 Infectious Substances (Hazard Class 6, Division 6.2)10.17.1 GeneralDivision 6.2 materials include infectious substances, biological products, regulated medical waste, sharps medical waste, used health care products, and forensic materials. Division 6.2 materials are not permitted in international mail or domestic mail, except when they are intended for medical or veterinary use, research, or laboratory certification related to the public health; and only when such materials are properly prepared for mailing to withstand shocks, pressure changes, and other conditions related to ordinary handling in transit. Mailable Division 6.2 materials sent as international mail must meet the standards in the International Mail Manual. For domestic mail, mailable Division 6.2 materials must meet the applicable standards in 10.17. Unless otherwise noted, all mailable Division 6.2 materials must meet the mail preparation requirements for air transportation. 10.17.2 DefinitionsThe terms used in the standards for Division 6.2 materials are defined as follows: a. Infectious substance means a material known or reasonably expected to contain a pathogen. A pathogen is a microorganism that can cause disease in humans or animals. Examples of pathogens include bacteria, viruses, fungi, and other infectious agents. An infectious substance must be assigned to one of the following two categories: 1. Category A: An infectious substance transported in a form capable of causing permanent disability or life-threatening or fatal disease in otherwise healthy humans or animals when exposure occurs. Category A infectious substances are not mailable. A Category A infectious substance is assigned the identification number UN 2814 or UN 2900, based on the known medical history or symptoms of the source patient or animal, endemic local conditions, or professional judgment concerning the individual circumstances of the source human or animal. 2. Category B: An infectious substance that does not meet the criteria for inclusion in Category A. A mailpiece known or suspected to contain a Category B infectious substance must bear the proper shipping name “Biological substance, Category B” on the address side of the mailpiece and must be assigned to and marked with identification number UN 3373 or, for regulated medical waste and sharps medical waste, identification number UN 3291. b. Biological product means a virus, therapeutic serum, toxin, antitoxin, vaccine, blood, blood component or derivative, allergenic product, or analogous product or arsphenamine or derivative of arsphenamine (or any other trivalent arsenic compound) intended to prevent, treat, or cure a disease or condition of humans or animals. A biological product includes a material subject to regulation under 42 U.S.C. 262 or 21 U.S.C. 151-159. Unless otherwise excepted, mark these mailpieces with identification number UN 3373 when they contain a biological product known or reasonably expected to contain a pathogen that meets the definition of a Category B infectious substance. c. Cultures are infectious substances that result from a process by which pathogens are intentionally propagated. This definition does not include a human or animal patient specimen as defined in 10.17.2e. d. Exempt human or animal specimen means a human or animal sample (including, but not limited to, secreta, excreta, blood and its components, tissue and tissue fluids, and body parts) transported for routine testing not related to the diagnosis of an infectious disease. Typically, exempt human specimens are specimens for which there is a low probability that the sample is infectious, such as specimens for drug or alcohol testing; cholesterol testing; blood glucose level testing; prostate-specific antigens (PSA) testing; testing to monitor heart, kidney, or liver function; pregnancy testing; and testing for diagnosis of noninfectious diseases such as cancer biopsies. Exempt human or animal specimens are not subject to regulation as hazardous materials but must be packaged according to 10.17.9. e. Patient specimen means material that is collected directly from humans or animals and transported for purposes such as diagnosis and research. Patient specimens include excreta, secreta, blood and its components, tissue and tissue swabs, body parts, and specimens in transport media (such as transwabs, culture media, and blood culture bottles). f. Regulated medical waste, for USPS purposes, means a soft waste material (other than a sharp) derived from the medical treatment, diagnosis, immunization, or biomedical research of a human or animal. Soft medical waste includes items such as used rubber gloves, swabs, gauze, tongue depressors, and other similar material. Mark these mailpieces with identification number UN 3291. g. Sharps medical waste, for USPS purposes, means a medical waste object that is capable of cutting or penetrating skin or packaging material and that is contaminated with a pathogen or may become contaminated with a pathogen derived from the medical treatment, diagnosis, immunization, or biomedical research of a human or animal. Sharps include used medical waste such as needles, syringes, scalpels, broken glass, culture slides, culture dishes, broken capillary tubes, broken rigid plastic, and exposed ends of dental wires. Mark these mailpieces with identification number UN 3291. h. Toxin means a Division 6.1 material from a plant, animal, or bacterial source. A toxin containing an infectious substance or a toxin contained in an infectious substance must be classed as Division 6.2, described as an infectious substance, and assigned to UN 2814, UN 2900, or UN 3373, as appropriate. A toxin known or suspected to contain a Category A infectious substance is not mailable. A toxin known or suspected to contain a Category B infectious substance must be marked UN 3373 and packaged under 10.17.5. Toxins from plant, animal, or bacterial sources that do not contain an infectious substance, and are not contained in an infectious substance, may be considered for classification as Division 6.1 toxic substances under 10.16. i. Used health care product means a medical, diagnostic, or research device or piece of equipment, or a personal care product used by consumers, medical professionals, or pharmaceutical providers that does not meet the definition of a diagnostic specimen, biological product, regulated medical waste, or sharps waste, is contaminated with potentially infectious body fluids or materials, and is not decontaminated or disinfected to remove or mitigate the infectious hazard prior to transport. 10.17.3 Nonregulated MaterialsThe following materials are not subject to regulation as Division 6.2 hazardous materials and are mailable when the packaging requirements in 10.17.8 are met: a. A biological product, including an experimental or investigational product or component of a product, subject to Federal approval, permit, review, or licensing requirements, such as those required by the Food and Drug Administration of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services or the U.S. Department of Agriculture. A biological product known or suspected to contain a Category B infectious substance must be marked UN 3373 and packaged under 10.17.4. A biological product known or suspected to contain a Category A infectious substance is not mailable. b. Blood collected for the purpose of blood transfusion or the preparation of blood products; blood products; plasma; plasma derivatives; blood components; tissues or organs intended for use in transplant operations; and human cell, tissues, and cellular and tissue-based products regulated under the Public Health Service Act (42 U.S.C. 264-272) or the Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (21 U.S.C. 332 et seq.). c. Blood, blood plasma, and blood components collected for the purpose of blood transfusion or the preparation of blood products and sent for testing as part of the collection process, except where the person collecting the blood has reason to believe it contains a Category B infectious substance, in which case the test sample must be shipped as a Category B infectious substance. Materials known or suspected to contain a Category A infectious substance are not mailable. d. Dried blood spots, collected by applying a drop of blood to absorbent material, or dried specimens for fecal occult blood detection. (These materials are not classified as exempt human or animal specimens.) e. Forensic material containing a biological material, such as tissue, body fluid, excreta, or secreta, not expected to contain a Category A or Category B infectious substance and transported on behalf of a U.S. Government agency or a state, local, or Indian tribal government agency. A forensic material known or suspected to contain a Category B infectious substance must be shipped as a Category B infectious substance. A forensic material known or suspected to contain a Category A infectious substance is not mailable.Packaging—General All materials mailable under the provisions in 10.17 must be properly packaged. Exhibit 10.17.3 lists the specific reference in 10.17 under which each type of mailable material must be packaged. Exhibit 10.17.3 Packaging Standards for Division 6.2 Infectious Substances
10.17.4 Packaging Category B Infectious SubstancesA material that is classified as a Category B infectious substance and that meets the definition in 10.17.2a..2. must be triple-packaged, meeting the packaging requirements in 49 CFR 173.199, and sent as First-Class Mail, Priority Mail, or Express Mail. Each primary receptacle containing a liquid must be leakproof and surrounded by absorbent material sufficient to protect the primary receptacle and absorb the total amount of liquid should the primary receptacle leak or break. Each primary receptacle containing a solid must be siftproof. Secondary containers for liquids must be leakproof. Secondary containers for solids must be siftproof. The primary and secondary packaging must be enclosed in a rigid outer shipping container. A single primary receptacle must not contain more than 1 liter (34 ounces) of a liquid specimen or 4 kg (8.8 pounds) of a solid specimen. Two or more primary receptacles whose combined volume does not exceed 4 liters (1 gallon) for liquids or 4 kg (8.8 pounds) for solids may be enclosed in a single secondary container. In addition: a. The secondary container must be marked with the international biohazard symbol shown in Exhibit 10.17.5d..3.. b. The primary receptacle or secondary packaging must be capable of withstanding, without leakage, an internal pressure producing a pressure differential of not less than 95 kPa (0.95 bar, 14 psi) in the range of -40° C to 55° C (-40° F to 130° F). c. All mailpieces sent under 10.17.4 must be marked on the address side with the shipping name “Biological substance, Category B” and “UN 3373” as outlined in 49 CFR 173.199 (a)(5). Regulated medical waste and sharps medical waste as defined in 10.17.2f. and 10.17.2g. must be marked UN 3291. See 10.17.5. d. Orientation arrows are not required on these mailpieces but may be used. e. The outer packaging must show the name and telephone number of a person who is knowledgeable about the material shipped and has comprehensive emergency response and incident mitigation information, or of someone who has immediate access to the person with such knowledge and information. 10.17.5 Sharps Waste and Other Mailable Regulated Medical WasteRegulated medical waste and sharps medical waste known or suspected to contain a Category A infectious substance is not mailable. Regulated medical waste and sharps medical waste as defined in 10.17.2f. and 10.17.2g., and containing materials classified as Category B infectious substances, must be marked UN 3291 and are permitted for mailing only using merchandise return service (see 505.3.0) with First-Class Mail or Priority Mail service, subject to the following requirements: a. Authorization. Each vendor of a complete regulated medical waste or sharps waste mailing container system (including all component parts required to safely mail such waste to a storage or disposal facility) must obtain authorization from the USPS prior to mailing. Before applying for authorization, each type of mailing container system must be tested and certified under the standards in 10.17.5e by an independent testing facility. The vendor in whose name the authorization is being sought must submit a written request to the manager, Product Classification, USPS Headquarters (see 608.8.0, USPS Contact Information, for address). The request for authorization must contain the following: 1. An irrevocable $50,000 surety bond or letter of credit as proof of sufficient financial responsibility to cover disposal costs if the vendor ceases doing business before all its waste container systems are disposed of or to cover cleanup costs if spills occur while the containers are in USPS possession. The surety bond or letter of credit must be issued in the name of the vendor seeking the authorization and must name the USPS as the beneficiary or obligee. Vendors that market their containers to distributors are responsible for disposal and cleanup costs attributed to those containers. In addition, vendors must provide a list of distributors, including firm names, addresses, and telephone numbers, to the Postal Service on request. 2. Address of the headquarters or general business office of the vendor seeking the authorization. 3. Name, address, and phone number of each storage and disposal site. 4. List of all types of mailing container systems to be covered by the request, a complete sample of each mailing container system, and proof of package testing certifications performed by the independent testing facility that subjected the packaging materials to the testing requirements in 10.17.5e. 5. Copy of the proposed waste shipping paper to be used with each mailing container system. 6. 24-hour toll free telephone number for emergencies. 7. List of the types of waste to be mailed for disposal in each mailing container system. 8. Copy of the merchandise return service label to be used with each mailing container system and verification that the merchandise return service permit fee and accounting fee have been paid. 9. Address of the Post Office or postage due unit where the containers are delivered. b. Packaging. Regulated medical waste and sharps medical waste that also meets the definition of a Category A infectious substance is not mailable. A medical waste material treated by steam sterilization, chemical disinfections, or other appropriate method so that it no longer contains a Category A or Category B infectious substance must be packaged under 10.17.8. The packaging for regulated medical waste and sharps medical waste containing or suspected of containing a Category B infectious substance is subject to these standards: 1. Sharps medical waste and regulated medical waste meeting the definitions in 10.17.2e and 10.17.2g must be collected in a rigid, securely sealed, and leakproof primary receptacle. For sharps waste, the primary receptacle must also be puncture-resistant and may not have a maximum capacity that exceeds 3 gallons in volume. For regulated medical waste, the primary receptacle may not have a maximum capacity that exceeds 5 gallons in volume. Each primary receptacle may not contain more than 50 ml (1.66 ounces) of residual waste liquid. Each primary receptacle must display the international biohazard symbol shown in Exhibit 10.17.5d3. Package testing results must show that the contents did not penetrate through the primary container during package testing and that the primary container can maintain its integrity at temperatures as low as 0°F and as high as 120°F. 2. The primary receptacle must be packaged within a watertight secondary container or containment system. The secondary container may consist of more than one component. If one of the components is a plastic bag, the bag must be at least 4 mil in thickness and must be used in conjunction with a fiberboard box. A plastic bag by itself does not meet the requirement for a secondary container. Several primary receptacles may be enclosed in a secondary container. The primary receptacle(s) must fit securely and snugly within the secondary container to prevent breakage during ordinary processing. 3. The secondary container must be enclosed in a strong outer shipping container constructed of 200-pound grade corrugated fiberboard. The joints and flaps of the outer shipping container must be securely taped, glued, or stitched to maintain the integrity of the container. When tape or glue is used to secure an outer shipping container, the material must be water-resistant. Fiberboard boxes with interlock bottom flaps (i.e., easy-fold) are not permitted as outer shipping containers unless reinforced with water-resistant tape. The secondary container must fit securely and snugly within the outer shipping container to prevent breakage during ordinary processing. 4. There must be enough material within the primary receptacle to absorb and retain three times the total liquid allowed within the primary receptacle (150 ml per primary receptacle) in case of leakage. 5. Each mailpiece must not weigh more than 25 pounds. Medical Professional Packages as identified in 10.17.5c., may not weigh more than 35 pounds. The container's maximum allowable weight must be printed on the outside of the box and on the assembly and closure instructions included with each mailpiece. The mailpiece must be tested at the maximum allowable weight identified by the vendor. 6. In each mailing container system, the authorized vendor must include a step-by-step instruction sheet that clearly details the proper sequence and method of container system assembly prior to mailing to prevent package failure during transport due to improper assembly. The instruction sheet must also include a customer service telephone number, or provide specific information on where such a telephone number is located elsewhere on the container system, for third-party end users to contact if they have assembly questions or find a component part is missing. c. Medical Professional Packages. Medical Professional Packages, while intended for use by small medical offices, is not limited to use by medical offices only. One primary receptacle larger than 5 gallons in volume may be used for mailing pre-primary sharps receptacles (sharps receptacles normally used in doctors' offices) and other regulated medical waste under the following conditions: 1. The mailpiece must meet all the requirements in 10.17.5 except for the primary receptacle capacity limits of 10.17.5b..1.. 2. Only rigid, securely closed, puncture and leak-resistant pre-primary sharps receptacles that meet or exceed Occupational Safety and Health Administration standards as identified in 29 CFR 1910.1030, may be placed inside the primary receptacle. Each pre-primary sharps container may contain no more than 50 ml (1.66 ounces) of residual waste liquid. Several pre-primary sharps receptacles may be enclosed in the single primary receptacle. 3. Multiple tie-closed plastic bags of regulated medical waste may be placed inside the single primary receptacle. 4. The primary receptacle must be lined with a plastic bag at least 4 mil in thickness and must include sufficient absorbent material within the liner to absorb all residual liquid in the primary receptacle. 5. The mailpiece must not weigh more than 35 pounds. d. Mailpiece Labeling, Marking, and Documentation. Regulated medical waste and sharps waste must meet the following requirements: 1. For Medical Professional Packages, the additional marking “Medical Professional Packaging” must be clearly printed in lettering at least 2 inches high on the address side of the outer shipping container. 2. Each primary receptacle and outer shipping container must bear a label, which cannot be detached intact, showing: (a) the company name of the vendor to which the mailing authorization is issued; (b) the USPS Authorization Number, and; (c) the container ID number (or unique model number) signifying that the packaging material is certified and that the vendor obtained the authorization required by 10.17.5a. Place the label on the top or on a side of the container. 3. The primary receptacle(s) and the outer shipping container must bear the international biohazard symbol in black with either a fluorescent orange or fluorescent red background as shown in Exhibit 10.17.5d3. The symbol on the outer shipping container must be at least 3 inches high and 4 inches wide.
Exhibit 10.17.5d3
International Biohazard Symbol
4. Each mailpiece must have a four-part waste shipping paper. The shipping paper must be affixed to the outside of the mailpiece in an envelope or similar carrier that can be easily opened and resealed to allow review of the document. The shipping paper must comply with all applicable requirements imposed by the laws of the state from which the container system is mailed. At a minimum, the information in Exhibit 10.17.5d4 must be on the shipping paper. Exhibit 10.17.5d4 Shipping Paper for Regulated Medical Waste and Sharps Waste Containers5. The outer shipping container must bear a properly prepared merchandise return service label (see 505.3.0). The merchandise return service permit must be held in the same name as that of the authorized medical waste vendor. 6. The outer shipping container must be marked on two opposite side walls with the package orientation marking in 49 CFR 173.312 to identify the proper upright position of the mailpiece during handling. 7. Mailpieces containing regulated medical waste or sharps waste must be marked on the address side with the correct UN number and proper shipping name (e.g., “Regulated Medical Waste, UN 3291” or “Regulated Medical Waste–Sharps, UN 3291”). 8. Vendors must retrieve mailpieces held at processing facilities due to improper labeling such as no return address or due to improperly completed shipping papers. e. Package Testing. Vendors must submit to the manager, Product Classification (see 608.8.0 for address), package testing results from an independent testing facility for each package for which the vendor is requesting authorization. In addition, vendors must submit package testing results from an independent testing facility when the design of a container system changes or every 24 months, whichever occurs first. The test results must show that if every mailpiece prepared for mailing were subject to the environmental and test conditions in 49 CFR and the additional test requirements in 10.17.5f, no contents would be released into the environment and the effectiveness of the packaging would not be significantly reduced. The Postal Service may require proof of accreditation or other documentation to support the credentials of an independent testing facility. f. Testing Criteria. Packages tested for approval as Medical Professional Packages may not be tested using pre-primary containers that are currently, or have previously been, approved as USPS primary containers. Test reports must identify by brand name the pre-primary containers used during testing. Each mailpiece must pass each of the tests described below: 1. Leak-proof test. The test must be conducted on one primary receptacle with the lid in place, without the secondary and outer packaging. The test duration must be at least 5 minutes and must be conducted at 20 kPa (3 psi). The pass/fail criterion is: no air leakage from anywhere other than the closure of the primary receptacle. Air leakage at the closure is not considered a failure if the primary receptacle passes the test for watertightness as determined by placing 50 ml of deionized water into the primary receptacle, securing the closure, and then turning the container on its side and observing for any evidence of leakage. Any evidence of water leaking from the primary receptacle is a failure. 2. Stacking test. One mailpiece must withstand the test in 49 CFR 178.606. The dynamic compression test must be conducted on the empty, unsealed mailpiece assembled for mailing, without the primary receptacle(s). The test mass is the vendor-identified maximum weight, not to exceed 25 pounds, as indicated on the outer shipping container and on the assembly and closing instructions. A compensation factor of 1.5 must be used to compute the test load, based on the vendor-identified weight. The pass/fail criteria are: no buckling of the sidewalls sufficient to cause damage to the contents in the primary receptacle, and in no case does the deflection exceed 1 inch. 3. Vibration test. One mailpiece filled with sharps or other regulated medical waste must withstand the test in 49 CFR 178.608. The test mailpiece is filled with sharps or other regulated medical waste to the vendor-identified maximum weight, not to exceed 25 pounds, as indicated on the outer shipping container and on the assembly and closing instructions. The test sample is prepared as it would be for mailing. The pass/fail criterion is: no rupture, cracking, or splitting of any primary receptacle. 4. Wet drop test. Five mailpieces filled with sharps or other regulated medical waste must withstand the test in 49 CFR 178.609e. Each test mailpiece is filled with sharps or other regulated medical waste to the vendor-identified maximum weight, not to exceed 25 pounds, as indicated on the outer shipping container and on the assembly and closing instructions included with each mailpiece. Each mailpiece is prepared as it would be for mailing and subjected to a water spray as described in the test. A separate, untested mailpiece is used for each drop orientation: top, longest side, shortest side, and corner. The pass/fail criteria are: no rupture, cracking, or splitting of any primary receptacle, and no contents may penetrate into or through the body or lid of any primary receptacle. 5. Cold drop test. Five mailpieces filled with sharps or other regulated medical waste must withstand the test in 49 CFR 178.609f. Each test mailpiece is filled with sharps or other regulated medical waste to the vendor-identified maximum weight, not to exceed 25 pounds, as indicated on the outer shipping container and on the assembly and closing instructions included with each mailpiece. Each mailpiece is prepared as it would be for mailing and chilled as described in the test. A separate, untested mailpiece is used for each drop orientation: top, longest side, shortest side, and corner. The pass/fail criteria are: no rupture, cracking, or splitting of any primary receptacle, and no contents may penetrate into or through the body or lid of any primary receptacle. 6. Impact test. One mailpiece filled with sharps or other regulated medical waste must withstand the test in 49 CFR 178.609h. The test mailpiece is filled with sharps or other regulated medical waste to the vendor-identified maximum weight, not to exceed 25 pounds, as indicated on the outer shipping container and on the assembly and closing instructions included with each mailpiece. The mailpiece is prepared as it would be for mailing. The pass/fail criteria are: no rupture, cracking, or splitting of any primary receptacle, and no contents may penetrate into or through the body or lid of any primary receptacle. 7. Puncture-resistant test. Package testing results must show that during all of the previous tests, the contents did not penetrate through the primary receptacle. 8. Temperature test. Package testing results must show that each primary receptacle maintained its integrity when exposed to temperatures as low as 0°F and as high as 120°F. 9. Absorbency test. Package testing results must show that the primary receptacle(s) contain enough absorbent material to absorb three times the total liquid allowed within the primary receptacle in case of leakage. Absorbency is determined by pouring 150 ml of deionized water into the primary receptacle(s), then turning the receptacle(s) upside down and observing for any evidence of free liquid not absorbed on contact. Any evidence of free liquid is a failure. 10. Watertight test. Package testing results must show that no leakage occurred when 50 ml of deionized water was placed into the secondary containment system and the entire system turned upside down for 5 minutes. g. Suspension of Authorization. The Postal Service may suspend a vendor's authorization based on information that a mailpiece no longer meets the standards for mailing sharps medical waste and regulated medical waste containers, or that the mailpiece poses an unreasonable safety risk to Postal Service employees or the public. The suspension can be made immediately, making the mailpiece nonmailable immediately. The vendor may contest a decision to suspend authorization by writing to the manager, Product Classification (see 608.8.0 for address), within 7 days from the date of the letter of suspension. The appeal should provide evidence demonstrating why the decision should be reconsidered. Any order suspending authorization remains in effect during an appeal or other challenge. When a vendor is notified that its authorization to mail sharps or other regulated medical waste containers has been suspended, the vendor must immediately: 1. Recall all identified containers. 2. Notify all customers that they cannot mail the identified containers. 3. Suspend sales and distribution of all identified containers. 4. Collect the identified containers from distributors, consumers, and the Postal Service without using the mail and in accordance with all federal and state regulations. 10.17.6 Packaging Used Health Care ProductsA used health care product known or reasonably suspected to contain a Category A material is not mailable. A used health care product not suspected to contain an infectious material, or that is known or suspected to contain a Category B infectious substance, and is being returned to the manufacturer or manufacturer's designee is mailable as First-Class Mail, Priority Mail, or Express Mail subject to the following packaging requirements: a. Each used health care product must be drained of liquid to the extent possible and placed in a watertight primary receptacle designed and constructed to ensure that it remains intact under normal conditions of transport. For a used health care product capable of cutting or penetrating skin or packaging material, the primary receptacle must be capable of retaining the product without puncture of the packaging under normal conditions of transport. The primary receptacle must be marked with the international biohazard symbol as shown in Exhibit 10.17.5d3. b. Each primary receptacle must be placed inside a watertight secondary container designed and constructed to ensure that it remains intact under normal conditions of transport. The secondary container must also be marked with the international biohazard symbol as shown in Exhibit 10.17.5d3. c. The secondary container must be placed inside an outer shipping container with sufficient cushioning material to prevent movement between the secondary container and the outer shipping container. An itemized list of the contents of the primary receptacle and information concerning possible contamination with a Division 6.2 material, including its possible location on the product, must be placed between the secondary container and the outer shipping container. A shipping paper and a content marking on the outer shipping container are not required. 10.17.7 Packaging Forensic MaterialForensic material containing a biological material, such as tissue, body fluid, excreta, or secreta, and sent on behalf of a U.S. Government agency or a state, local, or Indian tribal government agency must be packaged under 10.17.8 when it is not known or suspected to contain a Category A or Category B infectious substance. Forensic material known or suspected to contain a Category A infectious substance is not mailable. Forensic material known or suspected to contain a Category B infectious substance as identified in 10.17.4 is mailable as First-Class Mail, Priority Mail, or Express Mail when triple-packaged in a primary receptacle, secondary container, and a rigid outer shipping container as follows: a. The forensic material must be held within a securely sealed primary receptacle. The primary receptacle must be surrounded by sufficient absorbent material (for liquids) and cushioning material to protect the primary container from breakage. The absorbent material must be capable of taking up the entire liquid contents of the primary receptacle in case of leakage. The primary receptacle must be marked with the international biohazard symbol as shown in Exhibit 10.17.5d3. b. The primary receptacle and the absorbent and cushioning material must be enclosed in a watertight and securely sealed secondary container. The secondary container must also display the international biohazard symbol as shown in Exhibit 10.17.5d3. c. The secondary container must be firmly and snugly packed within a strong outer shipping container that is securely sealed. A shipping paper and a content marking on the outer shipping container are not required. 10.17.8 Packaging Nonregulated Materials
Nonregulated materials as defined in 10.17.3 are not subject to regulation as hazardous materials but must be properly packaged when presented for mailing. Regulated medical waste, sharps medical waste, and used health care products must be packaged and mailed under 10.17.5 and 10.17.6. Exempt human and animal specimens must be packaged under 10.17.9. Nonregulated materials are mailable as First-Class Mail, Priority Mail, Express Mail, or Package Services mail. Such materials must be held within a securely sealed primary receptacle. The primary receptacle must be surrounded by sufficient absorbent material (for liquids) and cushioning material to protect the primary receptacle from breakage. The absorbent material must be capable of taking up the entire liquid contents of the primary receptacle in case of leakage. Either the primary receptacle or the inner packaging must be marked with the international biohazard symbol shown in a. Liquid Patient Specimens and Biological Products. Mailers must package a liquid nonregulated patient specimen, a forensic specimen, or a biological product (such as polio vaccine) as follows: 1. Not exceeding 50 ml. A patient specimen or biological product consisting of 50 ml or less per mailpiece must be packaged in a securely sealed primary receptacle. Two or more primary receptacles whose combined volume does not exceed 50 ml may be enclosed within a single mailpiece. Sufficient absorbent material and cushioning material to withstand shock and pressure changes must surround the primary receptacle(s), or be otherwise configured to take up the entire liquid contents in case of leakage. The primary receptacle(s) and the absorbent cushioning must be enclosed in a secondary container with a leakproof barrier that can prevent failure of the secondary container if the primary receptacle(s) should leak during transport. The secondary container must be securely sealed, and it may serve as the outer shipping container if it has sufficient strength to withstand ordinary postal processing. The secondary container must be marked with the international biohazard symbol shown in Exhibit 10.17.5d3, except when the secondary container also serves as the outer shipping container. In that case, the biohazard symbol must appear on the inner packaging or on the primary container. A shipping paper and a content marking on the outer shipping container are not required. 2. Exceeding 50 ml. A liquid patient specimen, forensic material, or biological product that exceeds 50 ml must be packaged in a securely sealed primary receptacle. A single primary receptacle must not contain more than 500 ml of specimen. Two or more primary receptacles whose combined volume does not exceed 500 ml may be enclosed in a single secondary container. Sufficient absorbent material and cushioning material to withstand shock and pressure changes must surround the primary receptacle(s), or be otherwise configured to take up the entire liquid contents in case of leakage. The primary receptacle(s) and the absorbent cushioning must be enclosed in a secondary container with a leakproof barrier that can prevent failure of the secondary container if the primary receptacle(s) should leak during transport. The secondary container cannot serve as the outer shipping container. The secondary container must be marked with the international biohazard symbol shown in Exhibit 10.17.5d3. The secondary container must be securely and snugly enclosed in a fiberboard box or container of equivalent strength that serves as the outer shipping container. A shipping paper and a content marking on the outer shipping container are not required. b. Solid (or Dry) Specimen. A solid or dry specimen, such as a saliva swab, blood spot, fecal smear, culture or stock, or forensic material, must be completely dried before packaging in a mailing container or envelope. Cushioning material to withstand shock and pressure changes is required only if the dry specimen is placed in a breakable primary receptacle. When required, the cushioning material must surround the primary receptacle. The primary receptacle (and cushioning material, if required) must be enclosed in a secondary container with a siftproof barrier that can prevent failure of the secondary container if the primary receptacle breaks during shipment. The secondary container must be securely sealed, and it may serve as the outer shipping container if it has sufficient strength to withstand ordinary postal processing. The secondary container must be marked with the international biohazard symbol shown in Exhibit 10.17.5d3, except when the secondary container also serves as the outer shipping container. In that case, the biohazard symbol must appear either on the inner packaging or on the primary receptacle. A shipping paper and a content marking on the outer shipping container are not required. 10.17.9 Packaging Exempt Human or Animal SpecimensExempt human or animal specimens as defined in 10.17.2d. are not subject to regulation as hazardous materials but when presented for mailing must be triple-packaged in leakproof (for liquids) or siftproof (for solids) primary receptacles. Sufficient cushioning and absorbent materials must surround each primary receptacle containing liquid. Secondary containers for liquids must be leakproof. Secondary containers for solids must be siftproof. The primary and secondary packaging must be enclosed in a rigid outer shipping container. A single primary receptacle must not contain more than 500 ml of a liquid specimen or 500 grams of a solid specimen. Two or more primary receptacles whose combined volume does not exceed 500 ml (for liquids) or 500 grams (for solids) may be enclosed in a single secondary container. The secondary container cannot serve as the outer shipping container. The secondary container must be marked with the international biohazard symbol shown in Exhibit 10.17.5d3. The secondary container must be securely and snugly enclosed in a fiberboard box or container of equivalent strength that serves as the outer shipping container. A shipping paper is not required. The outer shipping container must be marked on the address side with the words “Exempt human specimen” or “Exempt animal specimen,” as appropriate. In addition, at least one surface of the outer packaging must have a minimum dimension of 3.9 inches x 3.9 inches (100 mm x 100 mm). Exempt human and animal specimens are mailable as First-Class Mail, Priority Mail, Express Mail, or Package Services mail. 10.18 Radioactive Materials (Hazard Class 7)Radioactive materials are prohibited in international mail and domestic mail if required to bear the DOT Radioactive White-I, Radioactive Yellow-II, or Radioactive Yellow-III label (49 CFR 172.436, 172.438, or 172.440, respectively) or if it contains quantities of radioactive material in excess of those authorized in Publication 52, Hazardous, Restricted, or Perishable Mail. Radioactive materials are prohibited in domestic mail via air transportation. For international mail, the standards in IMM 135 apply. 10.19 Corrosives (Hazard Class 8)10.19.1 DefinitionA corrosive is any liquid or solid that causes visible destruction or irreversible alteration in human skin tissue at the site of contact or a liquid that has a severe corrosion rate on steel. 10.19.2 MailabilityCorrosives are prohibited in international mail. A corrosive that can qualify as an ORM-D material is permitted in domestic mail via air or surface transportation subject to these limitations: a. Liquid Corrosive. A liquid mixture must be 1 pint or less and must contain 15% or less corrosive material with the remainder of the mixture not being a hazardous material, unless otherwise specified for a specific corrosive material. Primary receptacles must be securely sealed compatible glass bottles that are enclosed within securely sealed metal or plastic secondary containers. The secondary container must be packed within a strong outer shipping container that does not exceed 25 pounds per mailpiece. b. Solid Corrosive. A solid mixture must be 10 pounds or less per primary receptacle and must contain 10% or less corrosive material with the remainder of the mixture not being a hazardous material, unless otherwise specified for a specific corrosive solid. The primary receptacle(s) and secondary container must be securely sealed compatible siftproof containers packed in strong outer shipping container. The total weight of a mailable solid corrosive cannot exceed 25 pounds per mailpiece. 10.19.3 MarkingFor surface transportation, the mailpiece must be plainly and durably marked on the address side with “Surface Only” or “Surface Mail Only” and “ORM-D” immediately following or below the proper shipping name. For air transportation, the mailpiece must be plainly and durably marked on the address side with “ORM-D AIR” immediately following or below the proper shipping name and must bear a shipper's declaration for dangerous goods. 10.19.4 Nonspillable Wet Electric Storage BatteriesA battery containing liquid electrolyte is prohibited from mailing unless the battery casing is completely sealed to prevent the liquid corrosive from spilling during handling. Nonspillable batteries with UN2800 are prohibited in international mail, but may be sent as domestic mail via air or surface transportation under the following conditions: a. The nonspillable battery must be protected from short circuits, surrounded with sufficient cushioning material, and securely packaged in a strong fiberboard box that serves as the outer shipping container. b. The outer shipping container must be marked “NONSPILLABLE BATTERY, UN2800” on the address side. c. The nonspillable battery must be capable of withstanding the vibration and pressure differential tests cited in 49 CFR 173.159(d)(i) and (ii). d. Only one nonspillable battery is allowed per mailpiece and the weight of the mailpiece cannot exceed 25 pounds. 10.20 Miscellaneous Hazardous Materials (Hazard Class 9)10.20.1 DefinitionA miscellaneous hazardous material is a substance or article that presents a hazard during transportation but does not meet the definition of any other hazard class. Examples of miscellaneous hazardous materials (not all of which are mailable) include solid dry ice, elevated temperature substances, environmentally hazardous substances, life-saving appliances, and asbestos. 10.20.2 MailabilityA miscellaneous hazardous material is prohibited in international mail. A miscellaneous hazardous material that can qualify as an ORM-D material is permitted for domestic mail via air or surface transportation, subject to the applicable 49 CFR requirements. 10.20.3 MarkingFor surface transportation, the mailpiece must be plainly and durably marked on the address side with “Surface Only” or “Surface Mail Only” and “ORM-D” immediately following or below the proper shipping name. For air transportation, a mailable material must be plainly and durably marked on the address side with “ORM-D AIR” immediately following or below the proper shipping name and bear a shipper's declaration for dangerous goods. 10.20.4 Dry IceDry ice (carbon dioxide solid) is prohibited in international mail. Dry ice is permitted in the domestic mail via air or surface transportation when used as a refrigerant to cool the contents of a mailpiece. A mailpiece containing dry ice must be packed in a container that is designed to permit the release of carbon dioxide gas and prevent a build-up of pressure that could rupture the parcel. Containers must conform to 49 CFR 173.217 and 175.10(a)(13). Additionally, the following applies: a. Air Transportation Requirements. Each mailpiece may not contain more than 5 pounds of dry ice. The address side of each mailpiece must be clearly marked “Carbon Dioxide Solid, UN1845” or “Dry Ice, UN1845” along with the net weight of the dry ice and the identity of the contents being cooled. A shipper’s declaration prepared in triplicate and a DOT Class 9 warning label for miscellaneous hazardous materials must be affixed to the outside of the mailpiece. b. Surface Transportation Requirements. The amount of dry ice per mailpiece may exceed 5 pounds. The address side of each mailpiece must be clearly marked “Carbon Dioxide Solid” or “Dry Ice” and “Surface Only” or “Surface Mail Only” along with the net weight of the dry ice and the identity of the contents being cooled. A shipper’s declaration and a DOT Class 9 warning label are not required for the dry ice. 10.20.5 Primary Lithium (Non-Rechargeable) Cells and BatteriesSmall consumer-type primary lithium cells or batteries (lithium metal or lithium alloy) like those used to power cameras and flashlights are mailable with the following restrictions. Each cell must contain no more than 1.0 gram (g) of lithium content per cell. Each battery must contain no more than 2.0 g aggregate lithium content per battery. Additionally, each cell or battery must meet the requirements of each test in the UN Manual of Tests and Criteria, Part III, and subsection 38.3 as referenced in DOT's hazardous materials regulation at 49 CFR 171.7. All primary lithium cells and batteries must be mailed within a firmly sealed package separated and cushioned to prevent short circuit, movement, or damage. Except for batteries installed in equipment, they must be in a strong outer package. All outer packages must have a complete delivery and return address. Primary lithium cells and batteries are mailable as follows: a. Via surface transportation when the cells or batteries (not packed with or installed in equipment) are “in the originally sealed packaging.” They are forbidden aboard passenger aircraft. The outside of the package must be marked on the address side “Surface Mail Only, Primary Lithium Batteries - Forbidden for Transportation Aboard Passenger Aircraft.” The mailpiece must not exceed 5 pounds. b. Via surface or air transportation when the cells or batteries are properly packed with or properly installed in the equipment they operate and the mailpiece has no more than the number of batteries needed to operate the device. Cells or batteries properly installed in the device they operate must be protected from damage and short circuit, and the device must be equipped with an effective means of preventing accidental activation. The outside of the package must be marked on the address side “Package Contains Primary Lithium Batteries.” The mailpiece must not exceed 11 pounds. 10.20.6 Secondary Lithium-ion (Rechargeable) Cells and BatteriesSmall consumer-type lithium-ion cells and batteries like those used to power cell phones and laptop computers are mailable with the following restrictions. Each cell must contain no more than 1.5 g of equivalent lithium content per cell. Each battery must contain no more than 8.0 g aggregate quantity of equivalent lithium content per battery. Additionally, each cell or battery must meet the requirements of each test in the UN Manual of Tests and Criteria, Part III, and subsection 38.3 as referenced in the DOT's hazardous materials regulation at 49 CFR 171.7. All secondary lithium-ion cells and batteries must be mailed in a firmly sealed package separated and cushioned to prevent short circuit, movement, or damage. Except for batteries installed in equipment, they must be in a strong outer package. All outer packages must have a complete delivery and return address. These cells and batteries are mailable as follows: a. Via surface or air transportation when individual cells or batteries are mailed or when properly packed with or properly installed in the equipment they operate. Cells or batteries properly installed in the device they operate must be protected from damage and short circuit, and the device must be equipped with an effective means of preventing accidental activation. The outside of the package must be marked on the address side “Package Contains Lithium-ion Batteries (no lithium metal).” b. The mailpiece must not contain more than 3 batteries. 10.20.7 Damaged or Recalled BatteriesDamaged or recalled batteries are prohibited from mailing unless approved by the manager, Product Classification. Exhibit 10.20.7 Lithium Battery Mailability Chart
Note 1: Each primary cell must not contain more than 1g lithium content. Note 2: Each primary battery must not contain more than 2g lithium content.
Note 3: Each secondary cell must not contain more than 1.5g equivalent lithium content. Note 4: Each secondary battery must not contain more than 8g equivalent lithium content. Note 5: For secondary batteries (lithium-ion) there is a limit of 3 batteries per mailpiece. 10.21 Other Regulated Materials—Magnetized MaterialsA magnetized material is not classified within any of the nine hazard classes. Such material is regulated as a hazardous material only if offered for carriage on air transportation and when it has a magnetic field strength capable of causing the deviation of aircraft instruments. Regulated magnetized materials are mailable subject to the following limitations: a. Definition. A magnetized material is any article that has a magnetic field strength capable of causing the deviation of aircraft instruments. A magnetized material is regulated as a hazardous material when it is presented for air transportation and has a measurable magnetic field strength greater than 0.00525 gauss at 15 feet. Magnetized materials include magnets and magnetized devices such as magnetrons and light meters of sufficient strength to possibly cause erroneous aircraft compass readings. If the maximum field strength observed at a distance of 7 feet is less than 0.002 gauss or there is no significant compass deflection (less than 0.5 degree), the article is not restricted as a magnetized material. b. Mailability. Regulated magnetized material is prohibited in international mail. A material with a measurable magnetic field strength greater than 0.00525 gauss at 15 feet is prohibited from domestic mail via air transportation. Mailable materials must be packaged and marked as specified in Publication 52, Hazardous, Restricted, and Perishable Mail. Mailable material permitted via air transportation must bear a shipper’s declaration for dangerous goods. Magnetized material is not regulated as a hazardous material when transported via surface transportation. 11.0 Cigarettes and Smokeless Tobacco11.1 DefinitionsFor this standard, we define terms as follows: a. Cigarette: any roll of tobacco wrapped in paper or in any substance not containing tobacco and any roll of tobacco wrapped in any substance containing tobacco which, because of its appearance, the type of tobacco used in the filler, or its packaging and labeling, is likely to be offered to, or purchased by, consumers as a cigarette. The term cigarette includes roll-your-own-tobacco and excludes cigars. b. Smokeless tobacco: any finely cut, ground, powdered, or leaf tobacco that is intended to be placed in the oral or nasal cavity or otherwise consumed without being combusted. c. Cigar: any roll of tobacco wrapped in leaf tobacco or in any substance containing tobacco, unless, because of its appearance, the type of tobacco used in the filler, or its packaging and labeling, the product is likely to be offered to, or purchased by, consumers as a cigarette. d. Roll-your-own tobacco: any tobacco which, because of its appearance, type, packaging, or labeling, is suitable for use and likely to be offered to, or purchased by, consumers as tobacco for making cigarettes or cigars, or for use as wrappers thereof. e. Consumer testing: testing limited to formal data collection and analysis for the specific purpose of evaluating the product for quality assurance and benchmarking purposes of cigarette brands or sub-brands among existing adult smokers. f. State: any of the 50 states of the United States, the District of Columbia, and any commonwealth, territory, or possession of the United States. 11.2 NonmailabilityExcept as provided in 11.3, all cigarettes (including roll-your-own tobacco) and smokeless tobacco are nonmailable and shall not be deposited in or carried through the Postal Service mailstream. Nonmailable cigarettes and smokeless tobacco deposited in the mail are subject to seizure and forfeiture. Any nonmailable cigarettes and smokeless tobacco products seized and forfeited shall be destroyed or retained by the federal government for the detection or prosecution of crimes or related investigations and then destroyed. Senders of nonmailable cigarettes and smokeless tobacco may be subject to seizure and forfeiture of assets, criminal fines, imprisonment, and civil penalties. The Postal Service will not accept for delivery or transmit any package that it knows, or has reasonable cause to believe, contains nonmailable cigarettes or smokeless tobacco. If the Postal Service reasonably suspects that a mailer is tendering nonmailable cigarettes or smokeless tobacco, then the mailer bears the burden of proof in establishing eligibility to mail. The Postal Service has reasonable cause not to accept for delivery or transmit a package based on: a. A statement on a publicly available website, or an advertisement, by any person that the person will mail matter which is nonmailable under this section in return for payment; or b. The fact that the mailer or other person on whose behalf a mailing is being made is on the U.S. Attorney General's List of Unregistered or Noncompliant Delivery Sellers. 11.3 Mailability ExceptionsCigarettes and smokeless tobacco are mailable if one of the conditions in 11.4 through 11.8 is met. These exceptions only apply to domestic mail under 608.2.1, including mail sent from the United States to Army Post Office (APO), Fleet Post Office (FPO), and Diplomatic Post Office (DPO) addresses to which tobacco is not restricted (see 703.2.3.1), with the exception that delivery procedures for overseas military mail under the certain individuals exception in 11.6 may vary as practicable. These exceptions do not apply to the following: a. Mail treated as domestic under 608.2.2. b. International mail as defined in 608.2.3. c. Mail presented at APO, FPO, or DPO installations destined to addresses in the United States. 11.4 Mailing Within Noncontiguous StatesApplicable mailings may not be tendered through Pickup on Demand or Carrier Pickup services. Intra-Alaskan and intra-Hawaiian shipments of cigarettes or smokeless tobacco are mailable, provided that such mailings: a. Are presented in a face-to-face transaction with a postal employee within the state; b. Destinate in the same state of origin; c. Bear a valid complete return address that is within the state of origin; and, d. Are marked with the following exterior marking on the address side of the mailpiece: “INTRASTATE SHIPMENT OF CIGARETTES OR SMOKELESS TOBACCO.” 11.5 Exception for Business/Regulatory PurposesEligibility to mail and to receive mail under the business/regulatory purposes exception is limited to federal and state government agencies and legally operating businesses that have all applicable state and federal government licenses or permits and are engaged in tobacco product manufacturing, distribution, wholesale, export, import, testing, investigation, or research under the conditions in 11.5.1 to 11.5.3. 11.5.1 ApplicationEach customer seeking to mail cigarettes or smokeless tobacco under the business/regulatory purposes exception must complete an application letter requesting to mail under the business/regulatory purposes exception. a. The applicant must furnish: 1. Information about its legal status, any applicable licenses, and authority under which it operates; 2. Information about the legal status, any applicable licenses, and operational authority for all entities to which the applicant's mailings under this exception will be addressed; and 3. All locations where mail containing cigarettes and smokeless tobacco will be presented. b. The applicant must establish its and its recipients' eligibility as legally operating businesses that have all applicable state and federal government licenses or permits and are engaged in tobacco product manufacturing, distribution, wholesale, export, import, testing, investigation, or research; or, in the case of mailings for regulatory purposes, as a federal or state agency. Only those shipments containing otherwise nonmailable tobacco addressed to recipients on the customer's list of designated recipients are eligible for the business/regulatory purposes exception. c. Applications must be mailed to the manager, Pricing & Classification Service Center (PCSC), see 608.8.4.1 for address. The manager, PCSC, issues the initial agency decision of a determination of eligibility to mail under the business/regulatory purposes exception. A number is assigned to each letter of eligibility. d. The applicant must timely update the information in its application as necessary prior to conducting any mailing for as long as it continues to mail under the business/regulatory exception. e. Customers whose applications or amendments to existing applications are denied in whole or in part may appeal to the manager, Product Classification (see 608.8.0). f. Eligibility to mail under the business/regulatory purposes exception may be revoked by the manager, PCSC, in the event of failure to comply with any applicable rules and regulations. A customer may appeal an adverse initial decision to the manager, Product Classification (see 608.8.0). Decisions by the manager, Product Classification, to uphold the denial of an application or to revoke a customer's eligibility under the business/regulatory purposes exception may be appealed to the Judicial Officer under 39 C.F.R. Part 953. g. Upon written request by a state or federal agency, the manager, PCSC, may, in his or her discretion, waive certain application requirements for mailings entered by the requesting state or federal agency for regulatory purposes. h. Any determination of eligibility to mail under this exception shall lapse if the authorized mailer does not tender any mail under this exception within any three-year period. After that time, the affected mailer must apply for and receive new authorization for any mailings under this exception. 11.5.2 Mailing[1-22-12] Customers eligible to mail under the business/regulatory purposes exception may enter mailings of cigarettes and smokeless tobacco only at the locations specified in the customer's application. Applicable mailings may not be tendered through Pickup on Demand or Carrier Pickup services. Before mailing any shipment under this exception, the mailer must present proof that the PCSC has authorized the mailer to mail such shipments at that location. All mailings under the business/regulatory purposes exception must: a. Be entered in a face-to-face transaction with a postal employee (carrier pickup not permitted) as Express Mail with Hold for Pickup service, Express Mail with an Adult Signature service (see 503.8.0), or Priority Mail with an Adult Signature service; b. Be accompanied by a request for PS Form 3811 return receipt, which must bear the sender's PACT eligibility number issued by the PCSC in the return address block as well as the addressee's full name and address, and be made returnable to the PCSC, PACT Mailing Office (see 608.4.1 for address) c. Bear the marking “PERMITTED TOBACCO MAILING - DELIVER ONLY TO ADDRESSED BUSINESS/AGENCY - RECIPIENT MUST FURNISH PROOF OF AGE AND EMPLOYMENT” on the address side of the mailpiece (place the marking directly above, below, or to the left of the postage); d. Bear the business or government agency name and full mailing addresses of both the sender and recipient, both of which must match exactly those listed on the customer's application on file with the Postal Service. 11.5.3 DeliveryMailings bearing the marking for business/regulatory purposes can only be delivered to a verified employee of the addressee business or government agency. The recipient must show proof that he or she is an employee of the business or government identified as the addressee on the mailing label under the following conditions: a. The recipient must be an adult of at least the minimum age for the legal sale or purchase of tobacco products at the place of delivery. The recipient must furnish proof of age via a driver's license, passport, or other government-issued photo identification that lists age or date of birth. b. Once age and the recipient's identity as an employee of the addressee are established, the recipient must sign PS Form 3849 and PS Form 3811 in the appropriate signature blocks. If mailer's eligibility number is missing in the return address block of the PS Form 3811, the mailing must be returned to sender. 11.6 Exception for Certain IndividualsThe exception for certain individuals permits the mailing of small quantities of cigarettes or smokeless tobacco by individual adults to businesses or to other adults. Such shipments may include, but are not limited to, cigarettes and smokeless tobacco exchanged as gifts between individual adults and a damaged or unacceptable tobacco product returned by a consumer to the manufacturer. For purposes of this rule, “gifts” do not include products purchased by one individual for another from a third-party vendor through a mail-order transaction, or the inclusion of cigarettes or smokeless tobacco at no additional charge with other matter pursuant to a commercial transaction. Eligibility to mail under the certain individuals exception may be revoked by the manager, PCSC, in the event of failure to comply with any applicable rules and regulations. A customer may appeal an adverse initial decision to the manager, Product Classification (see 608.8.0). The mailer bears the burden of proof in establishing eligibility in the event of revocation. Decisions by the manager, Product Classification, to revoke a customer's eligibility under this exception may be appealed to the Judicial Officer under 39 C.F.R. Part 953. Mailings under this exception must be made under the conditions in 11.6.1through 11.6.3. 11.6.1 Entry and AcceptanceMailings under the certain individuals exception must be entered under the following conditions: a. Cigarettes or smokeless tobacco may only be mailed via a face-to-face transaction with a postal employee. Applicable mailings may not be tendered through Pickup on Demand or Carrier Pickup services. b. Cigarettes or smokeless tobacco may only be entered by an adult of at least the minimum age for the legal sale or purchase of tobacco products at the place of entry. c. The individual presenting the mailing must furnish government-issued photo identification that lists age or date of birth, such as a driver's license or passport, at the time of the mailing. The name on the identification must match the name of the sender appearing in the return address block of the mailpiece. d. For mailings addressed to an individual, at the time the mailing is presented, the customer must orally confirm that the addressee is an adult of at least the minimum age for the legal sale or purchase of tobacco products at the place of delivery. 11.6.2 Mailing[1-22-12] No customer may send or cause to be sent more than 10 mailings under this exception in any 30-day period. Each mailing under the certain individuals exception must: a. Be entered (carrier pickup not permitted) as Express Mail with Hold For Pickup service, Express Mail with an Adult Signature service (see 503.8.0), or Priority Mail with an Adult Signature service; unless shipped to APO/FPO/DPO addresses under 11.6.4. b. Bear the marking “PERMITTED TOBACCO MAILING — DELIVER ONLY TO AGE-VERIFIED ADULT OF LEGAL AGE” on the address side of the exterior of the mailpiece (place the marking directly above, below, or to the left of the postage); c. Bear the full name and mailing address of the sender and recipient on the Express Mail or Priority Mail label; d. Weigh no more than 10 ounces; 11.6.3 Delivery[1-22-12] Delivery under the certain individuals exception is made under the following conditions: a. The recipient receiving or signing for the article must be an adult of at least the minimum age for the legal sale or purchase of tobacco products at the place of delivery. b. The recipient must furnish proof of age via a driver's license, passport, or other government-issued photo identification that lists age or date of birth. c. For Express Mail or Adult Signature articles, once age is established, the recipient must sign PS Form 3849 in the appropriate signature block. 11.6.4 Tobacco Product Shipments to APO/FPO/DPOShipments of cigarettes and smokeless tobacco may not be sent to APO/FPO/DPO destination addresses to which the mailing of tobacco is restricted (see 703.2.3.1). To the extent cigarettes or smokeless tobacco are permitted to be mailed to APO/FPO/DPO destination addresses, such mailings under the certain individuals exception must comply with all of the requirements of 11.6, with the exception that mailings may be entered as either Express Mail Military Service (EMMS) or Priority Mail service with Delivery Confirmation. Regardless of the service elected, the mailing must bear the full name and mailing address of the sender and recipient. 11.7 Consumer Testing ExceptionThe exception for consumer testing permits a legally operating cigarette manufacturer or a legally authorized agent of a legally operating cigarette manufacturer to mail cigarettes to verified adult smokers solely for consumer testing purposes. The manufacturer for which mailings are entered under this exception must have a permit, in good standing, issued under 26 U.S.C. § 5713. The consumer testing exception applies only to cigarettes and not smokeless tobacco. Items must be mailed under conditions in 11.7.1through 11.7.3. 11.7.1 ApplicationEach customer seeking to mail cigarettes under the consumer testing exception must submit an application letter to mail under consumer testing exception. In support of its application, the following must be met: a. The applicant must furnish information to establish that the customer, or the customer's principal if the customer is a manufacturer's agent, is a cigarette manufacturer in good standing under 26 U.S.C. § 5713; if the customer is an agent of a manufacturer, complete details about the agency relationship with the manufacturer; and all locations where mail containing cigarettes for consumer testing will be presented. The applicant must timely update all information in its application as necessary prior to conducting any mailing for as long as it continues to mail under the consumer testing exception. b. As part of its application, the applicant must certify in writing that it will comply with the following requirements: 1. Any recipient of consumer testing samples of cigarettes is an adult established smoker; 2. No recipient has made any payment for the cigarettes; 3. Every recipient will sign a statement indicating that the recipient wishes to receive the mailings; 4. The manufacturer or the legally authorized agent of the manufacturer will offer the opportunity for any recipient to withdraw the recipient's written statement at least once in every three-month period; 5. Any package mailed under this exception will contain not more than 12 packs of cigarettes (maximum of 240 cigarettes) on which all taxes levied on the cigarettes by the state and locality of delivery have been paid and all related state tax stamps or other tax-payment indicia have been applied; and 6. The manufacturer will maintain records establishing compliance with these obligations for a three-year period from the date of each mailing. c. The application must be submitted to the manager, Pricing & Classification Service Center (PCSC) (see 608.4.1for address). d. The applicant must provide any requested copies of records establishing compliance to the manager, PCSC, and/or the manager, Product Classification (see 608.8.0), upon request no later than 10 business days after the date of the request. e. The manager, PCSC, issues the initial agency decision of a determination of eligibility to mail under the consumer testing exception. A number is assigned to each letter of eligibility. Customers whose applications are denied in whole or in part may appeal to the manager, Product Classification. Eligibility to mail under the consumer testing exception may be revoked by the manager, PCSC, in the event of failure to comply with any applicable rules and regulations. Decisions by the manager, Product Classification, to uphold the denial of an application or to revoke a customer's eligibility under the consumer testing exception may be appealed to the Judicial Officer under 39 C.F.R. Part 953. f. Any determination of eligibility to mail under this exception shall lapse if the authorized mailer does not tender any mail under this exception within any three-year period. After that time, the affected mailer must apply for and receive new authorization for any further mailings under this exception. 11.7.2 Mailing[1-22-12] Customers eligible to mail under the consumer testing exception may enter mailings of cigarettes only at the locations specified in the customer's application. Applicable mailings may not be tendered through Pickup on Demand or Carrier Pickup services. Mailings must be tendered under the following conditions: a. Before tendering any shipment under this exception, the mailer must present proof (PCSC Eligibility letter) that the PCSC has authorized the mailer to tender such shipments at that location. b. All mailings under the consumer testing exception: 1. Be entered in a face-to-face transaction with a postal employee (carrier pickup not permitted) as Express Mail with Hold For Pickup service, Express Mail with Adult Signature Restricted Delivery service (see 503.8.0), or Priority Mail with Adult Signature Restricted Delivery service; 2. Be accompanied by a request for PS Form 3811 return receipt, which must bear the sender's PACT eligibility number issued by the PCSC in the return address block, as well as the addressee's full name and address, and be made returnable to PCSC, PACT Mailing Office (see 608.4.1for address); 3. Must bear the marking “PERMITTED TOBACCO MAILING — DELIVER ONLY TO ADDRESSEE UPON AGE VERIFICATION — AGE 21 OR ABOVE” on the address side of the mailpiece (place the marking directly above, below, or to the left of the postage); 4. Must bear the full mailing addresses of both the sender and recipient on the Express Mail or Priority Mail label (the name and address of the sender must match exactly those listed on the customer's application on file with the PCSC); 5. Are limited in tobacco contents to no more than 12 packs of cigarettes (maximum 240 cigarettes) on which all taxes levied on the cigarettes by the destination state and locality have been paid and all related state tax stamps or other tax-payment indicia have been applied; 6. May not be addressed to an addressee located in a state that prohibits the delivery or shipment of cigarettes to individuals in the destination state; 7. May be sent only to an addressee who has not made any payment for the cigarettes, is being paid a fee for participation in consumer tests, and has agreed to evaluate the cigarettes and furnish feedback to the manufacturer in connection with the consumer test. c. Customers must maintain records to establish compliance with the requirements in 11.7 for a three year period. d. Mailing frequency may not exceed more than one package from any one manufacturer to an adult smoker during any 30-day period. e. Nothing in these rules shall preempt, limit, or otherwise affect any related state laws. 11.7.3 Delivery[1-22-12] Mailings bearing the marking for consumer testing can only be delivered to the named addressee under the following conditions: a. The recipient signing for the Express Mail Hold for Pickup service article must be an adult of at least 21 years of age. b. The recipient must furnish proof of age through production of a driver's license, passport, or other government-issued photo identification that lists age or date of birth. c. The name on the identification must match the name of the addressee on the Express Mail or Priority Mail label. d. Once age is established, the recipient must sign the PS Form 3849 and PS Form 3811 in the appropriate signature blocks. If mailer's eligibility number is missing in the return address block of the PS Form 3811 return receipt, the mailing must be returned to sender. 11.8 Public Health ExceptionFederal government agencies involved in the consumer testing of tobacco products solely for public health purposes may mail cigarettes under the mailing standards of 11.7, except as provided herein. The federal agency shall not be subject to the requirement that the recipient be paid a fee for participation in consumer tests. Upon written request, the manager, PCSC, may, in his or her discretion, waive certain of the application requirements. 12.0 Other Restricted and Nonmailable Matter12.1 Firearms12.1.1 Definitions[1-22-12] The terms used in this standard are defined as follows: a. Firearm means any device, including a starter gun, which will, or is designed to, or may readily be converted to, expel a projectile by the action of an explosive; the frame or receiver of any such weapon; any firearm muffler or firearm silencer; or any destructive device; but the term shall not include antique firearms (except antique firearms described under 12.1.1c and 12.1.1d). b. Firearm frame or receiver is the part of a firearm which provides housing for the hammer, bolt or breechblock, and firing mechanism, and which is usually threaded at its forward portion to receive the barrel. c. Handgun (including pistols and revolvers) means any firearm which has a short stock and is designed to be held and fired by the use of a single hand and subject to 12.1.1a, or a combination of parts from which a handgun can be assembled. d. Other firearms capable of being concealed on the person include, but are not limited to, short-barreled shotguns and short-barreled rifles. e. Short-barreled shotgun means a shotgun that has one or more barrels less than 18 inches long. The term short-barreled rifle means a rifle that has one or more barrels that are less than 16 inches long. These definitions include any weapon made from a shotgun or rifle, whether by alteration, modification, or otherwise, if such weapon as modified has an overall length of less than 26 inches. A short-barreled shotgun or rifle of greater dimension may be regarded as nonmailable when it has characteristics to allow concealment on the person. f. Federal Firearms Licensee (FFL) manufacturer, dealer, or importer of firearms means a manufacturer, dealer, or importer duly licensed by the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives (ATF) under Chapter 44, Title 18, United States Code (U.S.C.). g. Curio and relic collector means an individual licensed by ATF to transfer or receive only those firearms defined as curios or relics by ATF under Title 27, Code of Federal Regulations (CFR), section 478.11. h. Antique firearm means any muzzle loading rifle/shotgun/pistol, which is designed to use black powder or a black powder substitute, and which cannot use fixed ammunition (except those that incorporate a firearm frame or receiver, any firearm which is converted into a muzzle loading weapon, or any muzzle loading weapon which can be readily converted to fire fixed ammunition by replacing the barrel, bolt, breechblock, or any combination thereof); or any firearm (including those with a matchlock, flintlock, percussion cap, or similar type of ignition system) manufactured on or before 1898, or any replica thereof, if such replica: 1. Is not designed or redesigned for using rimfire or conventional centerfire fixed ammunition. 2. Uses rimfire or conventional centerfire fixed ammunition that is no longer manufactured in the United States and that is not readily available in the ordinary channels of commercial trade. i. Air gun means a gun that fires a projectile by means of compressed air or other gas (including paintball and pellet guns). 12.1.2 HandgunsHandguns and other firearms capable of being concealed on the person are nonmailable unless mailed between the parties listed in 12.1.3 and 12.1.5 after the filing of an affidavit or statement required by 12.1.4 and 12.1.6, and are subject to the following: a. Firearms meeting the definition of a handgun under 12.1.1b, and the definition of curios or relics under 27 CFR 478.11 may be mailed between curio and relic collectors only when those firearms also meet the definition of an antique firearm under 12.1.1h. b. Firearms meeting the definition of a handgun under 12.1.1b which are certified by the curator of a municipal, state, or federal museum which exhibits firearms to be curios or relics of museum interest may be accepted for mailing without regard to 12.1.3 through 12.1.6. c. Air guns that do not fall within the definition of firearm under 12.1.1a that are capable of being concealed on a person are mailable; but must include adult signature service under 503.8.0. Mailers must comply with all applicable state and local regulations. d. Parts of handguns are mailable, except for handgun frames, receivers or other parts or components regulated under Chapter 44, Title 18, U.S.C. e. Mailers are also subject to applicable restrictions by governments of a state, territory, or district. 12.1.3 Authorized PersonsSubject to 12.1.4, handguns may be mailed by a licensed manufacturer of firearms, a licensed dealer of firearms, a licensed importer of firearms, or an authorized agent of the federal government or the government of a state, territory, or district, only when addressed to a person in one of the following categories for use in the person's official duties: a. Officers of the Army, Coast Guard, Air Force, Navy, Marine Corps, or Organized Reserve Corps. b. Officers of the National Guard or militia of a state, territory, or district. c. Officers of the United States or of a state, territory, or district, whose official duty is to serve warrants of arrest or commitment. d. USPS employees authorized by the Chief Postal Inspector. e. Officers and employees of enforcement agencies of the United States. f. Watchmen engaged in guarding the property of the United States, a state, territory, or district. g. Purchasing agent or other designated member of agencies employing officers and employees included in 12.1.3c. through 12.1.3e. 12.1.4 Affidavit of AddresseeAny person proposing to mail a handgun under 12.1.3 must file with the postmaster, at the time of mailing, an affidavit signed by the addressee setting forth that the addressee is qualified to receive the firearm under a particular category of 12.1.3a through 12.1.3g, and that the firearm is intended for the addressee’s official use. The affidavit must also bear a certificate stating that the firearm is for the official duty use of the addressee, signed by one of the following, as appropriate: a. For officers of Armed Forces, by the commanding officer. b. For officers and employees of enforcement agencies, by the head of the agency employing the addressee to perform the official duty with which the firearm is to be used. c. For watchmen, by the chief clerk of the department, bureau, or independent branch of the government of the United States, the state, the territory, or the district by which the watchman is employed. d. For the purchasing agent or other designated member of enforcement agencies, by the head of such agency, that the firearm is to be used by an officer or employee included in 12.1.3c through 12.1.3e, Authorized Persons. 12.1.5 Manufacturers, Dealers, and ImportersHandguns may also be mailed between licensed manufacturers of firearms, licensed dealers of firearms, and licensed importers of firearms in customary trade shipments, or for repairing or replacing parts. 12.1.6 Certificate of Manufacturers, Dealers, and ImportersA federal firearms licensee manufacturer, dealer or importer need not file the affidavit under 12.1.4, but must file with the postmaster a statement on Form 1508 signed by the mailer that he or she is a licensed manufacturer, dealer or importer of firearms. The mailer must also state that the parcels containing handguns, or parts and components of handguns under 12.1.2d, are being mailed in customary trade shipments or contain such articles for repairing or replacing parts, and that to the best of their knowledge the addressees are licensed manufacturers, dealers or importers of firearms. 12.1.7 Federal and Other Law Enforcement AgenciesHandguns may be mailed without regard to 12.1.3 through 12.1.6 if the item is: a. Addressed to a scientific laboratory or crime detection bureau of any federal, state or local law enforcement agency whose members are authorized to serve warrants of arrest or commitment. b. Sent by an authorized agent of the federal government as an official shipment to any qualified addressee in 12.1.3, or to a licensed manufacturer, dealer, or importer of firearms, or to a federal agency. 12.2 Rifles and ShotgunsExcept under 12.1.1d and 12.1.2, unloaded rifles and shotguns are mailable. Mailers must comply with the rules and regulations under 27 CFR, Part 478, as well as state and local laws. The mailer may be required by the USPS to establish, by opening the parcel or by written certification, that the rifle or shotgun is unloaded and not ineligible for mailing under 12.1.1d. The following conditions also apply: a. Subject to state, territory, or district regulations, rifles and shotguns may be mailed without restriction when sent within the same state of mailing. These items must bear a “Return Service Requested” endorsement, and must be sent by Express Mail (“signature required” must be used at delivery), Registered Mail, or must include either insured mail service (for more than $200) requiring a signature at delivery. b. A shotgun or rifle owned by a non-FFL may be mailed outside the owner's state of residence by the owner to himself or herself, in care of another person in the state, where he or she intends to hunt or engage in any other lawful activity. These mailpieces must: 2. Include the “in the care of” endorsement immediately preceding the name of the applicable temporary custodian. 3. Be opened by the rifle or shotgun owner only. 4. Be mailed using services described in 12.2a.. c. Rifles and shotguns may be mailed by a non-FFL owner domestically to a FFL dealer, manufacturer, or importer in any state. USPS recommends these items be mailed using those services described in 12.2a.. d. Except as described in 12.1.2a, licensed curio and relic collectors may mail firearms meeting the definition of curios or relics under 27 CFR 478.11 domestically to FFL licensed curio and relic collectors in any state. USPS recommends these items be mailed using those services described in 12.2a.. e. Firearms which are certified by the curator of a municipal, state, or federal museum which exhibits firearms to be curios or relics of museum interest may be accepted for mailing without restriction. f. Air guns that do not fall within the definition of firearm under 12.1.1a are mailable. A shipment containing an air gun with a muzzle velocity of 400 or more feet per second (fps) must include an Adult Signature service under 503.8.0. Mailers must additionally comply with all applicable state and local regulations. 12.3 Legal Opinions on Mailing FirearmsPostmasters are not authorized to give opinions on the legality of any shipment of firearms. Further advice and ATF contact information is available at http://www.atf.gov/firearms/faq/. 12.4 Replica or Inert Explosive DevicesReplica or inert explosive devices that bear a realistic appearance to explosive devices such as simulated grenades, but that are not dangerous, are permitted in the mail when all of the following conditions are met: a. The package is presented by the mailer at a retail counter. b. Registered Mail service is used. (Registered Mail service is only available for items mailed as either First-Class Mail or Priority Mail.) c. The address side of the package is labeled with “REPLICA EXPLOSIVE” using at least 20 point type or letters at least 1/4-inch high. 12.5 Knives and Sharp Instruments12.5.1 MailabilityKnives (including sharp-pointed instruments such as stilettos that lack cutting edges) with a blade that opens automatically by hand pressure applied to a button or other device in the handle, or by operations of inertia, gravity, or both, or with a detachable blade propelled by a spring-operated mechanism, are mailable only when sent to: a. The respective government’s or organization’s designated supply or procurement officers and employees ordering, procuring, or buying such knives for use with the activities of the federal government; the National Guard, the Air National Guard, or the militia of a state, territory, or the District of Columbia; or the municipal government of the District of Columbia or of the government of any state or territory, or of any county, city, or other political subdivision of a state or territory. b. Manufacturers of such knives, or bona fide dealers of such knives, in connection with a shipment made under an order from any person designated in 12.5.1a. 12.5.2 Addressee IdentificationBefore delivering a shipment (or parcel) that contains an article or articles described in 12.5.1, a USPS employee may require that the recipient identify himself or herself as in one of the categories in 12.5.1a. 12.5.3 WrappingSharp-pointed or sharp-edged instruments such as knives, tools, ice picks, and razor blades, that are otherwise mailable, must be wrapped to protect their points and edges from cutting through the outer carton in which they are mailed. 12.6 Prohibited Parcel MarkingFor any parcel containing a firearm or a ballistic or switchblade knife, any marking that indicates the contents is not permitted on the outside wrapper or container. 12.7 Intoxicating LiquorA potable beverage is nonmailable if it is of 0.5% or more alcoholic content by weight, which is taxable under Chapter 51, Internal Revenue Service Code. The product may be mailed if it conforms to applicable requirements of the Internal Revenue Service and Food and Drug Administration and is not an alcoholic beverage, poisonous, or flammable. 12.8 Matter Emitting Obnoxious OdorAny matter that is a source of an obnoxious odor is nonmailable. 12.9 Liquids and Powders12.9.1 Liquids and SemisolidsLiquids and semisolids that may liquefy under normal conditions and are otherwise mailable must be adequately prepared for mailing under 1.0 through 8.0. 12.9.2 PowdersPowders that, if allowed to escape from their containers, could cause damage, discomfort, destruction, or soiling, must either be packed in siftproof containers or in other containers sealed in durable siftproof outer containers. 12.10 Motor Vehicle Master Keys and Locksmithing Devices12.10.1 Motor Vehicle Master Key—DefinitionA motor vehicle master key is any key (other than the key furnished by the manufacturer with the motor vehicle, or the key furnished with a replacement lock, or an exact duplicate of such keys) designed to operate two or more motor vehicle ignition, door, or trunk locks of different combinations, including any pattern, impression, or mold from which such a master key can be made (18 USC 1716A; 39 USC 3002). 12.10.2 NonmailableAny motor vehicle master key, as defined in 12.10.1, and any advertisement for the sale of such item, are nonmailable, unless sent to any of the following: c. Motor vehicle manufacturer or dealer. d. Federal, state, or local government agency. 12.10.3 MarkingAny marking identifying the contents is not permitted on the outside wrapper or container of any parcel containing motor vehicle master keys. 12.10.4 Locksmithing Device—DefinitionA locksmithing device is: a. A device or tool (other than a key) designed to manipulate the tumblers in a lock into the unlocked position through the keyway of such lock. b. A device or tool (other than a key or a device or tool under 12.10.4a) designed for bypassing a lock or similar security device, or for opening it by a method normally not used by consumers to open such locks or security devices. c. A device or tool designed for making an impression of a key or similar security device to duplicate such key or device. 12.10.5 NonmailableAny locksmithing device, as defined in 12.10.4, is nonmailable, unless sent to any of the following: a. Lock manufacturer or distributor. d. Motor vehicle manufacturer or dealer. e. Bona fide automotive repair shops or businesses. 12.11 Drugs12.11.1 Over-the-Counter DrugsOver-the-counter drugs are medicines that can be obtained without a prescription. Over-the-counter drugs may be mailed when all applicable federal, state, and local laws, such as the Poison Prevention Packaging Act of 1970 and the Consumer Product Safety Commission requirements, are followed. 12.11.2 Prescription DrugsPrescription drugs are licensed medicines that require a written order by a medical doctor or pharmacist before they can be obtained. Prescription drugs, including those that contain controlled substances, may be mailed by drug manufacturers or their registered agents, pharmacies, or other authorized dispensers as permitted by 21 CFR 1307.12 or in compliance with any regulation of the Food and Drug Administration or other applicable law. 12.11.3 Controlled SubstancesControlled substances are any anabolic steroid, narcotic, hallucinogenic, stimulant, or depressant drug in Schedules I through V of the Controlled Substances Act, 21 USC 801 and 21 CFR 1300. Controlled Substances may be mailed by drug manufacturers or their agents, pharmacies, or other authorized dispensers when distribution is lawful under 21 USC 801 and 21 CFR 1300 and if the mailer or the addressee meets one of the following conditions: a. The mailer or the addressee is registered with the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA). b. The mailer or the addressee is exempt from DEA registration in performing official duties such as military, civil defense, and law enforcement personnel. 12.11.4 Packaging and MarkingsSecurely package all mailable drugs so that the contents cannot become damaged or dislodged during mailing. Follow the general packaging instructions in 601.1.0 through 601.8.0. Do not identify the nature of the contents on the outside of the mailpiece. 12.11.5 Return of Prescription DrugsMailers may use merchandise return service to return prescription drugs for purposes of drug recalls; voluntary manufacturer withdrawals; and dispensing errors such as incorrect drug, dosage, or strength, as permitted by 21 CFR 1307.12 or other applicable law. The mailpiece must be addressed to the manufacturer or its registered agent. Manufacturers or their registered agents must furnish mailing containers to their customers for the purpose of mailing back the identified drugs. Manufacturers or their registered agents must use merchandise return service (see 505.3.0) with First-Class Mail or Priority Mail for these mailpieces. Manufacturers or their agents continue to be responsible for maintaining records in compliance with any regulation of the Drug Enforcement Administration and/or the Food and Drug Administration. 12.11.6 Mailing StandardsIf distribution of a controlled substance is lawful under 21 USC 801, et seq., and any implementing regulation in 21 CFR 1300, et seq., the USPS considers such distribution by mail to constitute the mailing of matter not outwardly or of its own force dangerous or injurious to a person's life or health and accordingly mailable, subject to these standards: a. The inner container of any package containing controlled substances is marked and sealed under the applicable provisions of the Controlled Substances Act (21 USC 801, et seq., and any implementing regulation in 21 CFR 1300, et seq.) and placed in a plain outer mailing container or securely overwrapped in plain paper. b. If the mailing includes prescription drugs containing controlled substances, the inner container is also labeled to show the prescription number and the name and address of the pharmacy, practitioner, or other person dispensing the prescription. c. The outer mailing wrapper or container is free of markings that indicate the nature of the content. 12.12 Drug Paraphernalia12.12.1 Definition and ExamplesIt is unlawful to use domestic or international mail to transport drug paraphernalia. The term drug paraphernalia refers to any equipment, product, or material of any kind primarily intended or designed for use in manufacturing, compounding, converting, concealing, producing, processing, preparing, injecting, ingesting, inhaling, or otherwise introducing into the human body a controlled substance, possession of which is unlawful under the Controlled Substances Act. Examples of drug paraphernalia are items primarily intended or designed for use in ingesting, inhaling, or otherwise introducing marijuana, cocaine, hashish, hashish oil, PCP, or amphetamines into the human body, such as metal, wooden, acrylic, glass, stone, plastic, or ceramic pipes with or without screens, permanent screens, hashish heads, or punctured metal bowls; water pipes, chamber pipes, carburetor pipes, electric pipes, ice pipes or chillers, and air-driven pipes; carburetion tubes and devices; smoking and carburetion masks; roach clips (i.e., objects used to hold burning material that is too small or short to be held in the hand); miniature spoons with level capacities of 1/10 cubic centimeter or less; chillums; bongs; wired cigarette papers; and cocaine freebase kits. 12.12.2 DeterminationIn determining whether an item constitutes drug paraphernalia, in addition to all other logically relevant factors, these factors may be considered: a. Oral or written instructions or other descriptive materials provided with the item that explain or depict its use. b. National and local advertising on its use. c. The manner in which the item is displayed for sale. d. Whether the owner, or anyone in control of the item, is a legitimate supplier of like or related items to the community, such as a licensed distributor or dealer of tobacco products. e. Direct or circumstantial evidence of the ratio of sales of the items to the total sales of the business enterprise. f. The existence and scope of legitimate uses of the item in the community. g. Expert testimony on its use. 12.12.3 ExceptionsThe standards in 12.12.1 and 12.12.2 apply neither to any person authorized by local, state, or federal law to manufacture, possess, or distribute items described in 12.12.1 and 12.12.2; nor to any item that, in the normal lawful course of business, is sold through the mail and traditionally intended for use with tobacco products, including any pipe, paper, or accessory. 12.13 Household SubstanceA household substance (39 USC 3001(f)), i.e., any matter unsolicited by the addressee, that contains a substance as defined by section 2 of the Poison Prevention Packaging Act of 1970 (15 USC 1471(2)), is permitted in the mail only if it complies with the requirements for special child-resistant packaging established for that substance by the Consumer Product Safety Commission (16 CFR 1700). 12.14 PesticideA pesticide (18 USC 1716), i.e., any matter that contains a pesticide as defined by section 2 of the Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act (7 USC 136(u)), is permitted in the mail only if it complies with child-resistant packaging standards established by the Environmental Protection Agency applicable to that particular matter (40 CFR 157) and meets the applicable standards in 10.0, Hazardous Materials. 12.15 Fragrance Advertising SampleA fragrance advertising sample (39 USC 3001(g)), i.e., any matter normally acceptable in the mail but containing a fragrance advertising sample, is permitted in the mail only if it is sealed, wrapped, treated, or otherwise prepared in a manner reasonably designed to prevent individuals from being unknowingly or involuntarily exposed to the sample. A sample meets this requirement if it uses paper stocks with a maximum porosity of 20 Sheffield units or 172 Gurley-Hill units treated exclusively with microencapsulated oils, and if the sample is produced so that it cannot be activated except by opening a glued flap or binder or by removing an overlying ply of paper. 12.16 Compliance CertificateA mailer who presents matter that is generally permitted in the mail under 12.13, 12.14, and 12.15 but for compliance with the specified packaging and preparation requirements may submit an accompanying written statement certifying that the matter is packaged or prepared under the applicable federal laws and postal standards. The certifying statement may be made on the mailer's letterhead, on a postage statement, or as a notice on the exterior of each item presented for mailing. 12.17 Battery-Powered DevicesCells or batteries properly installed in equipment must be protected from damage and short circuit, and equipment or devices containing cells or batteries must include an effective means of preventing accidental activation. A battery with liquid electrolyte is not permitted in the mail unless it is a nonspillable type battery that meets the standards in 10.0, Hazardous Materials. 12.18 Abortive and Contraceptive Devices12.18.1 Abortion DevicesAny article or thing designed, adapted, or intended for producing abortion is not permitted in the mail (18 USC 1461). 12.18.2 ContraceptivesUnsolicited samples of an article or thing designed, adapted, or intended for preventing conception is permitted in the mail only when sent to a manufacturer or a dealer of such an article or things, to a licensed physician or surgeon, or to a nurse, pharmacist, druggist, hospital, or clinic (39 USC 3001; 18 USC 1461). 12.19 Building Construction MaterialBuilding construction material is not permitted in the mail if the acceptance and processing is likely to harm or injure USPS employees, mail, or equipment. Factors considered include but are not limited to whether the material may pose potential storage problems at the postal facilities that may process the material; whether the volume of material may impede the flow of mail in USPS transportation or mail distribution systems; whether the volume of material may lead to security problems; and whether processing the material may create safety hazards for USPS employees. 12.20 Prohibition on Sharp Instruments Intended for Use in an Animal Fighting VentureThe interstate or international mailing of a knife, a gaff, or any other sharp instrument attached, or designed or intended to be attached, to the leg of a bird for use in an animal fighting venture (as defined in section 9.3.1b) is prohibited (7 U.S.C. 2156). Violators can be subject to the criminal penalties in 18 U.S.C. 49. See 9.3.1 for the prohibition on mailing animals intended for use in an animal fighting venture and 13.5.7 for the restrictions on mailing written, printed, or graphic matter related to animal fighting ventures. 12.21 Mail Weighing More Than 13 OuncesA mailpiece weighing more than 13 ounces bearing only postage stamps as postage may not be deposited into a collection box, Postal Service lobby drop, Automated Postal Center (APC) drop, Postal Service dock, customer mailbox, or other unattended location. These mailpieces are also precluded from pickup service. The sender must present such items to an employee at a retail service counter in a Postal Service facility. Improperly presented items will be returned to the sender for proper entry and acceptance. 13.0 Written, Printed, and Graphic Matter Generally13.1 Solicitations in Guise of Bills, Invoices, or Statements of Account (39 USC 3001(D); 39 USC 3005)13.1.1 GeneralAny otherwise mailable matter that reasonably could be considered a bill, invoice, or statement of account due, but is in fact a solicitation for an order, is nonmailable unless it conforms to 13.1.2 through 13.1.5 in Solicitations in Guise of Bills, Invoices, or Statements of Account (39 USC 3001(D); 39 USC 3005). A nonconforming solicitation constitutes prima facie evidence of violation of 39 USC 3005. Compliance with this section does not avoid violation of Section 3005 if any part of the solicitation or any information with it misrepresents a material fact to the addressee (e.g., misleading the addressee about the identity of the sender of the solicitation or about the nature or extent of the goods or services offered may be a violation of Section 3005). 13.1.2 Required DisclaimerThe solicitation must bear on its face either the disclaimer required by 39 USC 3001(d)(2)(A) or the notice: “THIS IS NOT A BILL. THIS IS A SOLICITATION. YOU ARE UNDER NO OBLIGATION TO PAY THE AMOUNT STATED ABOVE UNLESS YOU ACCEPT THIS OFFER.” The statutory disclaimer or the alternative notice must be displayed in conspicuous boldface capital letters of a color prominently contrasting with the background against which it appears, including all other print on the face of the solicitation and that are at least as large, bold, and conspicuous as any other print on the face of the solicitation, but not smaller than 30-point type (see Exhibit 13.1.2). The notice or disclaimer required by this section must be displayed conspicuously apart from other print on the page immediately below each portion of the solicitation that reasonably could be construed to specify a monetary amount due and payable by the recipient. It must not be preceded, followed, or surrounded by words, symbols, or other matter that reduces its conspicuousness or that introduces, modifies, qualifies, or explains the required text, such as “Legal Notice Required by Law.”
Exhibit 13.1.2
Solicitation Disclaimer 13.1.3 IntelligibilityThe notice or disclaimer must not, by folding or any other device, be made unintelligible or less prominent than any other information on the face of the solicitation. 13.1.4 Separable PagesIf a solicitation consists of more than one page or if any page is designed to be separated into portions (e.g., by tearing along a perforated line), the notice or disclaimer required by 13.1.2 must be displayed in its entirety on the face of each page or portion of a page that might be reasonably considered a bill, invoice, or statement of account due as required by 13.1.2. 13.1.5 DefinitionsFor this standard, color prominently contrasting excludes any color, or any intensity of an otherwise included color, that does not permit legible reproduction by ordinary office photocopying equipment used under normal operating conditions, and which is not at least as vivid as any other color on the face of the solicitation; and color includes black. 13.2 Solicitations Deceptively Implying Federal Connection, Approval, or Endorsement (39 USC 3001(H) and 3001(I); 39USC3005)13.2.1 USPS EndorsementAny solicitation stating that it is approved by the USPS or the Postmaster General or that it conforms to any postal law or regulation is nonmailable. 13.2.2 Nonmailable by Government MisrepresentationA solicitation that misrepresents a government entity is nonmailable subject to these conditions: a. Matter that contains a solicitation for products, services, information, or funds that implies any federal government connection, approval, or endorsement through the use of a seal, insignia, reference to the Postmaster General, citation to a federal statute, name of a federal agency, department, or commission, or program, trade, or brand name, or any other term or symbol; or contains any reference to the Postmaster General or a citation to a federal statute that misrepresents either the identity of the mailer or the protection or status afforded such matter by the federal government is nonmailable unless it conforms to 13.2.3. A nonconforming solicitation constitutes prima facie evidence of violation of 39 USC 3005. Compliance with 13.2.3 does not avoid violation of 39 USC 3005 if the solicitation or accompanying information misrepresents material fact such as the nature, value, quantity, quality, or efficacy of the products or services offered for sale, or of the activities of an organization asking for information or monetary contributions. b. Such solicitations must not contain a false representation that federal government benefits or services will be affected by whether or not the recipient makes a purchase or contribution. c. Solicitations for payment for services otherwise available to the recipient free of charge from the federal government are nonmailable unless they contain a clear and conspicuous statement giving notice of that fact. 13.2.3 Permitted SolicitationsA solicitation described in 13.2.2a may be mailable if it meets at least one of these conditions (see Exhibit 13.2.3b): a. The solicitation is by a nongovernmental entity that actually has the federal government connection, approval, or endorsement implied by the solicitation’s terms or symbols. b. The solicitation appears in a publication for which the addressee has paid or promised to pay a consideration or which the addressee has otherwise indicated he or she wants to receive, and the solicitation is not on behalf of the publisher of the publication.
Exhibit 13.2.3b
Disclaimers for Solicitations Implying Federal Connection
c. The solicitation displays the notice required by 13.2.3c..1. on the envelope or outside cover or wrapper in which the solicitation is mailed, and one of the two notices required by 13.2.3c..2. on the contents. These notices must be printed in boldface capital letters of a color prominently contrasting with the background against which they appear. “Color prominently contrasting” excludes any color or intensity that ordinary photocopying cannot reproduce legibly. The color, which can include black, must be at least as vivid as any other color on the face of the solicitation and its envelope or outside cover or wrapper. The required wording, type size and style, and placement for the notices are as follows: 1. On the Envelope, Cover, or Wrapper. The face of the envelope or outside cover or wrapper must bear the notice: “THIS IS NOT A GOVERNMENT DOCUMENT.” The letters for printing this notice must be as large, bold, and conspicuous as any other letters on the face of such envelope, cover, or wrapper, but never smaller than 12-point type. The notice must appear in the upper right quadrant, below the postage stamp or other postage indicia and above the address, and it must be surrounded by a clear space not less than 1/4 inch wide. 2. On the Contents. The solicitation mailed within the envelope, cover, or wrapper must bear at the outset on its face one of these two headlines, depending on its purpose as indicated in parentheses: (a) “THIS PRODUCT OR SERVICE HAS NOT BEEN APPROVED OR ENDORSED BY THE FEDERAL GOVERNMENT, AND THIS OFFER IS NOT BEING MADE BY AN AGENCY OF THE FEDERAL GOVERNMENT” (for the purchase of or payment for a product or service); (b) “THIS ORGANIZATION HAS NOT BEEN APPROVED OR ENDORSED BY THE FEDERAL GOVERNMENT, AND THIS OFFER IS NOT BEING MADE BY AN AGENCY OF THE FEDERAL GOVERNMENT” (for information or the contribution of funds or membership fees). The letters for printing these notices must be as large, bold, and conspicuous as any other letters on the face of the solicitation, but never smaller than 30-point type. The notice must be surrounded by a clear space at least 1/2 inch wide. The notice must not be preceded, followed, or surrounded by words, symbols, or other matter that reduces its conspicuousness or introduces, modifies, qualifies, or explains the required text, such as “Notice Required by Law.” The notice must not, by folding or any other device, be made unintelligible or less prominent than any other information on the face of the solicitation. 13.3 Lottery Matter (18 USC 1302)13.3.1 DefinitionFor this standard, lottery is any scheme or promotion, whether lawful under the laws of any state, which, on paying a consideration, offers a prize dependent in whole or in part on lot or chance. 13.3.2 Unlawful Mail MatterUnlawful matter includes any letter, newspaper, periodical, parcel, stamped card or postcard, circular, or other matter permitting or facilitating participation in a lottery; any lottery ticket or part thereof or substitute; and any form of payment for a lottery ticket or share. 13.3.3 Fishing Contests, Indian Gaming Regulatory Act, LotteriesThis standard does not apply to: a. Any fishing contest not conducted for profit, in which prizes are awarded for the species, size, weight, or quality of fish caught by contestants in any bona fide fishing or recreational event (18 USC 1305). b. Mailings, to addresses within a state, of tickets or other material on a lottery conducted by that state under its laws (18 USC 1307). c. Any gaming conducted by an Indian tribe under the Indian Gaming Regulatory Act (25 USC 2720). d. An advertisement, list of prizes, or other information on a lottery not prohibited by the state where it is conducted. 13.4 Advertising Matter13.4.1 RestrictionsAny advertising, promotional, or sales matter that solicits or induces the mailing of any article described in 8.0, 9.0, or 10.0 is nonmailable except that such matter relating to controlled substances, radioactive materials, restricted liquids and powders, battery-powered devices, odd-shaped items in envelopes, and switchblade and ballistic knives, as described in 8.0, 9.0, or 10.0, is mailable if it contains packaging instructions and any other mailing limitations under 8.0 through 13.0, 508.9.0, Pandering Advertisements, and 508.10.0, Sexually Oriented Advertisements, (18 USC 1716). 13.4.2 Master KeysAdvertisements for motor vehicle master keys are nonmailable (18 USC 1716A, 39 USC 3002), except to lock manufacturers, professional locksmiths, motor vehicle manufacturers or dealers; and federal, state, or local government agencies. 13.5 Other Nonmailable Matter13.5.1 Fictitious NameMatter addressed to a person using a fictitious name, title, or address in conducting, through the mail, any scheme or device in violation of law is nonmailable if: a. After notification, the addressee fails to appear at the Post Office and be identified. b. The fictitious character of such mail is established to the Judicial Officer’s satisfaction in consequence of a proceeding initiated under 39 CFR 953 (18 USC 1342). 13.5.2 Foreign OriginMail of foreign origin is nonmailable if it contains matter determined by a court of competent jurisdiction or by the International Trade Commission to violate the Semiconductor Chip Protection Act of 1984 (17 USC 901-914) or to violate the copyright laws of the United States or any copyright convention or treaty to which the United States is a party (17 USC 601-603). 13.5.3 Foreign DestinationMatter addressed to foreign countries posted in violation of law or treaty stipulation is nonmailable. 13.5.4 Lewd or Filthy MatterObscene, lewd, lascivious, or filthy publications or writings, or mail containing information on where, how, or from whom such matter may be obtained, and matter that is otherwise mailable but that has on its wrapper or envelope any indecent, lewd, lascivious, or obscene writing or printing, and any mail containing any filthy, vile, or indecent thing is nonmailable (18 USC 1461, 1463). 13.5.5 Matter Inciting ViolenceAny matter of a character tending to incite arson, murder, assassination, treason, insurrection, or forcible resistance to any law of the United States, or containing any threat to take the life of, or to inflict harm upon, the President of the United States is nonmailable (18 USC 1461, 1717). 13.5.6 Other MatterOther matter that is nonmailable (18 USC 1717) includes every letter, writing, circular, stamped card or postcard, picture, print, engraving, photograph, newspaper, pamphlet, book, publication, or thing as described in these statutes: a. Forged or altered military or official passes (18 USC 499). b. Matter bearing forged or altered seals of government departments or agencies (18 USC 506). c. Defense information (18 USC 793, 794). d. Documents obtained by persons falsely assuming to be foreign diplomats (18 USC 915). e. False statements influencing foreign governments (18 USC 954). f. Matter relating to a conspiracy to injure property of a foreign government (18 USC 956). g. Matter unlawfully in aid of a foreign government (18 USC 957). h. Matter relating to an expedition against a friendly nation (18 USC 960). i. Matter relating to delivery of an armed vessel to a belligerent nation (18 USC 964). j. Matter wrongfully bearing the seal of a government department or agency (18 USC 1017). k. Forged, altered, or misused passports (18 USC 1543, 1544). Passport applications containing false statements, and passports falsely obtained (18 USC 1542). l. Matter bearing false statements intended to injure Armed Forces during war (18 USC 2388). 13.5.7 Restriction on Matter Related to Animal Fighting VenturesThis standard does not pertain to written, printed, or graphic matter related to fighting ventures involving live birds if such fight is permitted under the laws of the state in which the fight is to take place (7 U.S.C. 2156). The terms animal, animal fighting venture, and state are defined in 9.3.1. Written, printed, or graphic matter is nonmailable if it: a. advertises an animal for use in an animal fighting venture; b. advertises a knife, a gaff, or any other sharp instrument attached, or designed or intended to be attached, to the leg of a bird for use in an animal fighting venture; or c. promotes or in any other manner furthers an animal fighting venture. 13.5.8 Private Identification Without DisclaimerA private identification document without a disclaimer is nonmailable (18 USC 1738; 39 USC 3001(a)). This group includes any document that: a. Is of a type intended or commonly accepted for the identification of individuals; b. Bears a birth date or age purported to be that of the person named in it; c. Is not issued by or under the authority of a government; d. Is deposited in the mail by someone in the business of furnishing, for valuable consideration, documents that meet criteria in 13.5.8a and 13.5.8c; e. Is deposited in the mail to further that business; and f. Is deposited by someone who knows that it fails to carry diagonally printed, clearly and indelibly on both the front and back, “NOT A GOVERNMENT DOCUMENT” in capital letters no smaller than 12-point type. 13.6 Sweepstakes Matter (39 USC § 3001(K)(3)(A))13.6.1 DefinitionThe term sweepstakes means a game of chance for which no consideration is required to enter. 13.6.2 Mailable MatterSweepstakes matter is mailable only if it discloses all of the following: a. In the body, in the rules, and on the order or entry form that no purchase is necessary. b. In the body, in the rules, and on the order or entry form that a purchase will not increase the odds of winning. c. All terms and conditions, including rules and entry procedures of the sweepstakes. d. The sponsor or mailer, with the principal place of business or address at which the sponsor or mailer may be contacted. e. Sweepstakes rules, including the odds of winning, quantity, value, and nature of the prize and the schedule of any payments over time. 13.6.3 Nonmailable MatterSweepstakes matter is nonmailable if it does any of the following: a. Represents that individuals not making a purchase may be disqualified from receiving future solicitations. b. Requires that the entry be accompanied by an order or payment for a product or service previously ordered. c. Represents that the recipient has won a prize unless that individual has won such prize. d. Otherwise contradicts or is inconsistent with any disclosure required by 13.6.2, Mailable Matter, or 13.6.3, Nonmailable Matter. 13.7 Skill Contests (39 USC 3001(K)(3)(B))13.7.1 DefinitionThe term skill contest means a puzzle, game, competition, or other contest in which a prize is awarded, the outcome depends upon the skill of the contestant, and for which a payment, purchase, or donation is required to enter. 13.7.2 Mailable MatterSkill contests are mailable only if they include all of the following: a. Disclose the terms and conditions of the contest, including the rules and entry procedures. b. Disclose the sponsor or mailer, with the principal place of business or address at which the sponsor or mailer may be contacted. c. Contain rules that state all of the following: 1. Number of rounds or levels and the cost to enter each round. 2. If subsequent rounds will be more difficult. 3. Maximum cost to enter all rounds. 4. Number of entrants or percentage expected to correctly solve the contest. 5. Identity or qualifications of the judges, if judged by other than the sponsor. 7. Dates the winners will be determined and the prizes awarded. 8. Quantity, value, and nature of the prize. 9. Schedule of any payments over time. 13.8 Facsimile Check (39 USC § 3001(K)(3)(C))A facsimile check is nonmailable unless it states on the face of the check that it is not a negotiable instrument and has no cash value. 13.9 Exclusions and Disclosures (39 USC §§ 3001(K)(4) & 3001(K)(5))13.9.1 Mailable MatterMatter described in 13.6, 13.7, and 13.8 is mailable if it appears in a magazine, newspaper, or other periodical if the promotions are not directed to a named individual, or the promotions do not include the opportunity to make a payment or order a product or service. 13.9.2 Notices and DisclaimersAny notice or disclaimer required under 13.6, 13.7, and 13.8 shall be clearly and conspicuously displayed. Disclaimers required by 13.6.2a and 13.6.2b must be more conspicuously displayed than any other disclaimer. 13.10 Removal of Names from Mailing Lists (39 USC § 3001(L))13.10.1 ListsIn general, any person who uses the mails for any mailing falling under 13.2, 13.6, 13.7, and 13.8 shall adopt reasonable practices or procedures to prevent the mailing of such matter to any person who, personally or through their legal representative, submits a written request that no such matter shall be mailed to that person. Such request may be made either to the mailer, or the Attorney General, or their representative, of the appropriate state. Such requests shall be honored for a period of five years from the date of the request. The mailer shall maintain a record of all such written requests. 13.10.2 Special Requirements for Sweepstakes and Skill ContestsAny promoter of sweepstakes or skill contests must make a clear and conspicuous disclosure of the address or toll-free telephone number by which an individual, or their duly authorized representative, may notify a promoter to have that individual's name and address removed from all lists of names and addresses used by that promoter to mail any skill contest or sweepstakes. Promoters have 60 days from the date of receipt of the removal request to effect the removal of the name and address from all mailing lists used by that promoter for any skill contest or sweepstakes. 13.11 Unauthorized Decisions by PostmastersPostmasters are not authorized to decide whether written, printed, or graphic matter is nonmailable based on its content or to deny entry to such matter or exclude it from the mail. 13.12 Refusal Due to Improper PreparationWritten, printed, or graphic matter not properly prepared for mailing can be refused. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||